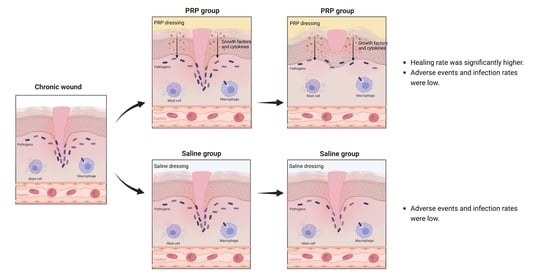
The Efficiency and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Dressing in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Research
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Outcome Measure
2.5. Assessment of Methodological Quality
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias
3.4. The Complete Healing Rate
3.5. Infection Rate and Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.-S.; Chen, S.-N. Apoptotic cell: Linkage of inflammation and wound healing. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dabas, M.M.; Schwartz, M.D.; Beeckman, D.; Gefen, A. Application of Artificial Intelligence Methodologies to Chronic Wound Care and Management: A Scoping Review. Adv. Wound Care 2023, 12, 205–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diegelmann, R.F.; Evans, M.C. Wound healing: An overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanic, S.; Deacon, J.M.; Chen, I.A. The Chronic Wound Phageome: Phage Diversity and Associations with Wounds and Healing Outcomes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0277721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidova-Rice, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R.; Herman, I.M. Acute and Impaired Wound Healing: Pathophysiology and current methods for drug delivery, part 1: Normal and chronic wounds: Biology, causes, and approaches to care. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2012, 25, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berlanga-Acosta, J.; Schultz, G.S.; López-Mola, E.; Guillen-Nieto, G.; García-Siverio, M.; Herrera-Martínez, L. Glucose Toxic Effects on Granulation Tissue Productive Cells: The Diabetics’ Impaired Healing. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 256043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Huang, S.; Dong, Y.; Xu, H.; Rong, Y.; Zhu, W.; et al. Clinical Studies on Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Chronic Cutaneous Ulcers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Wound Care 2022, 11, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monika, P.; Chandraprabha, M.N.; Rangarajan, A.; Waiker, P.V.; Murthy, K.N.C. Challenges in Healing Wound: Role of Complementary and Alternative Medicine. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 791899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, K.; Ma, X.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, W.; Gao, C.; Pu, Y.; Luo, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y. Innate Immunity in Diabetic Wound Healing: Focus on the Mastermind Hidden in Chronic Inflammatory. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 653940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.K.; Mattke, S.; Sheridan, M.; Ennis, W. Association of wound healing with quality and continuity of care and sociodemographic characteristics. Am. J. Manag. Care 2022, 28, e146–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, A.; Yuan, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Recent trends on burn wound care: Hydrogel dressings and scaffolds. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4523–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.E.; Foster, D.S.; Longaker, M.T. Management of Chronic Wounds—2018. JAMA 2018, 320, 1481–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasathkumar, M.; Sadhasivam, S. Chitosan/Hyaluronic acid/Alginate and an assorted polymers loaded with honey, plant, and marine compounds for progressive wound healing—Know-how. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 656–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, E.D.A.; De Medeiros, W.M.T.Q.; Pontes, T.P.D.A.; Barbosa, M.M.; De Araújo, A.A.; De Araújo, R.F.J.; Figueiredo, J.G.; Leitão, R.C.; Martins, C.D.S.; Da Silva, F.O.N.; et al. Chitosan Membrane Modified With a New Zinc(II)-Vanillin Complex Improves Skin Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, Q. Carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogels containing fibroblast growth factors for triggering diabetic wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 287, 119336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xing, F.; Luo, R.; Liu, M. Clinical Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Long-Bone Delayed Union and Nonunion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 771252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntragulpoontawee, M.; Chang, K.-V.; Vitoonpong, T.; Pornjaksawan, S.; Kitisak, K.; Saokaew, S.; Kanchanasurakit, S. The Effectiveness and Safety of Commonly Used Injectates for Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection Treatment of Peripheral Nerve Entrapment Syndromes: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Xiang, Z.; Rommens, P.M.; Ritz, U. 3D Bioprinting for Vascularized Tissue-Engineered Bone Fabrication. Materials 2020, 13, 32429135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xing, F.; Luo, R.; Duan, X. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Bone Fracture Treatment: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence in Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 676033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-Y.; Huang, C.-F.; Lin, T.-C.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y.T.; Liu, A.; Chen, W.-H.; Wei, H.-J.; Wang, M.-F.; Williams, D.F.; et al. Delayed animal aging through the recovery of stem cell senescence by platelet rich plasma. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9767–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, G.; Sellberg, F.; Sommar, P.; Ronaghi, M.; Lubenow, N.; Knutson, F.; Berglund, D. Standardizing the freeze-thaw preparation of growth factors from platelet lysate. Transfusion 2017, 57, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Lang, L.; Lingjiao, H.; Wei, C.; Zhou, X. Platelet-rich plasma has better mid-term clinical results than traditional steroid injection for plantar fasciitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2021, 107, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odem, M.A.; Bavencoffe, A.G.; Cassidy, R.M.; Lopez, E.R.; Tian, J.; Dessauer, C.W.; Walters, E.T. Isolated nociceptors reveal multiple specializations for generating irregular ongoing activity associated with ongoing pain. Pain 2018, 159, 2347–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, D.; Lv, Y. Autologous Platelet-Rich Gel for the Treatment of Diabetic Sinus Tract Wounds: A Clinical Study. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 247, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uçar, Ö.; Çelik, S. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma gel in the care of the pressure ulcers with the dressing with serum physiology in terms of healing process and dressing costs. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Game, F.; Jeffcoate, W.; Tarnow, L.; Jacobsen, J.L.; Whitham, D.J.; Harrison, E.F.; Ellender, S.J.; Fitzsimmons, D.; Löndahl, M.; Dhatariya, K.; et al. LeucoPatch system for the management of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers in the UK, Denmark, and Sweden: An observer-masked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Tulder, M.W.; Assendelft, W.J.J.; Koes, B.W.; Bouter, L.M. Method Guidelines for Systematic Reviews in the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group for Spinal Disorders. Spine 1997, 22, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oremus, M.; Wolfson, C.; Perrault, A.; Demers, L.; Momoli, F.; Moride, Y. Interrater Reliability of the Modified Jadad Quality Scale for Systematic Reviews of Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Trials. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2001, 12, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senet, P.; Bon, F.-X.; Benbunan, M.; Bussel, A.; Traineau, R.; Calvo, F.; Dubertret, L.; Dosquet, C. Randomized trial and local biological effect of autologous platelets used as adjuvant therapy for chronic venous leg ulcers. J. Vasc. Surg. 2003, 38, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Driver, V.R.; Hanft, J.; Fylling, C.P.; Beriou, J.M. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of autologous platelet-rich plasma gel for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Ostomy Wound Manag. 2006, 52, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Anitua, E.; Aguirre, J.J.; Algorta, J.; Ayerdi, E.; Cabezas, A.I.; Orive, G.; Andia, I. Effectiveness of autologous preparation rich in growth factors for the treatment of chronic cutaneous ulcers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 84, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Reffat, S.A.; Hassan, A.; Eskander, F. Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Clean Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 38, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardeñosa, M.E.; Domínguez-Maldonado, G.; Córdoba-Fernández, A. Efficacy and safety of the use of platelet-rich plasma to manage venous ulcers. J. Tissue Viability 2017, 26, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Moneib, H.; Youssef, S.S.; Aly, D.G.; A Rizk, M.; I Abdelhakeem, Y. Autologous platelet-rich plasma versus conventional therapy for the treatment of chronic venous leg ulcers: A comparative study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgarhy, L.H.; El-Ashmawy, A.A.; Bedeer, A.E.; Al-Bahnasy, A.M. Evaluation of safety and efficacy of autologous topical platelet gel vs platelet rich plasma injection in the treatment of venous leg ulcers: A randomized case control study. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaid, A.; El-Said, M.; Emile, S.; Youssef, M.; Khafagy, W.; Elshobaky, A. Randomized Controlled Trial on Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Saline Dressing in Treatment of Non-healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers. World J. Surg. 2020, 44, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.; Järbrink, K.; Divakar, U.; Bajpai, R.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J. The humanistic and economic burden of chronic wounds: A systematic review. Wound Repair Regen. 2019, 27, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinengo, L.; Olsson, M.; Bajpai, R.; Soljak, M.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J.; Järbrink, K. Prevalence of chronic wounds in the general population: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammons, M.C.B.; Morrissey, K.; Tripet, B.P.; Van Leuven, J.T.; Han, A.; Lazarus, G.S.; Zenilman, J.M.; Stewart, P.S.; James, G.A.; Copié, V. Biochemical Association of Metabolic Profile and Microbiome in Chronic Pressure Ulcer Wounds. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canesso, M.C.C.; Vieira, A.T.; Castro, T.B.R.; Schirmer, B.G.A.; Cisalpino, D.; Martins, F.S.; Rachid, M.A.; Nicoli, J.R.; Teixeira, M.M.; Barcelos, L.S. Skin Wound Healing Is Accelerated and Scarless in the Absence of Commensal Microbiota. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5171–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, E.; Liu, P.Y.; Schultz, G.S.; Martins-Green, M.M.; Tanaka, R.; Weir, D.; Gould, L.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Gibbons, G.W.; Wolcott, R.; et al. Chronic wounds: Treatment consensus. Wound Repair Regen. 2022, 30, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, M.F.P.; Miguel, S.P.; Cabral, C.S.D.; Correia, I.J. Hyaluronic acid—Based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, N.; Nasser, H.; Salvatore, L.; Natali, M.L.; Campa, L.; Mahmoud, M.; Capobianco, L.; Sannino, A.; Madaghiele, M. Hyaluronic acid for advanced therapies: Promises and challenges. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Islam, J.; Ray, S.; Raju, P.S.; Mazumder, B. Aspects of Nanomaterials in Wound Healing. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbern, S. Identifying Pain and Effects on Quality of Life from Chronic Wounds Secondary to Lower-Extremity Vascular Disease: An Integrative Review. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2018, 31, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodas, G.; Soler-Rich, R.; Rius-Tarruella, J.; Alomar, X.; Balius, R.; Orozco, L.; Masci, L.; Maffulli, N. Effect of Autologous Expanded Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells or Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma in Chronic Patellar Tendinopathy (With Gap >3 mm): Preliminary Outcomes After 6 Months of a Double-Blind, Randomized, Prospective Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 1492–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Zhou, C.; Hui, D.; Du, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Pu, X.; Gu, L.; Liu, L.; et al. Hyaluronic acid as a bioactive component for bone tissue regeneration: Fabrication, modification, properties, and biological functions. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 1059–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfahl, A.M.; El Baky, A.M.A.; Yousef, M.T.; Elgohary, H.M. High Versus Low Frequency Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation on Chronic Venous Lower Limb Ulceration Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Li, S.; Yin, D.; Xie, J.; Rommens, P.M.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, M.; Ritz, U. Recent progress in Mg-based alloys as a novel bioabsorbable biomaterials for orthopedic applications. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2022, 10, 1428–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.A.; Richards, T.; Srai, S.K.S. The role of iron in the skin and cutaneous wound healing. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, F.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Long, C.; Wu, L.; Lei, H.; Kong, Q.; Fan, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Zhang, X. Regulation and Directing Stem Cell Fate by Tissue Engineering Functional Microenvironments: Scaffold Physical and Chemical Cues. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 2180925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Xing, F.; Luo, R.; Liu, M. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and meta-Analysis of Current Evidence in Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossart, S.; Jafari, S.M.S.; Lehmann, M.; Jossi-Will, A.; Sane, E.; Heidemeyer, K.; Schorno, P.; Pelloni, L.; Rammlmair, A.; Schlapbach, C. Effect of topical application of platelet-rich plasma on chronic venous leg ulcerations. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.-P.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Lee, H.-L.; Hsu, T.-Y.; Chang, Y.-T.; Shen, Y.-A. Enhanced Platelet-Rich Plasma (ePRP) Stimulates Wound Healing through Effects on Metabolic Reprogramming in Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Hu, X. Platelet-derived respiratory-competent mitochondria transfer to mesenchymal stem cells to promote wound healing via metabolic reprogramming. Platelets 2022, 33, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemetson, K.J.; Clemetson, J.M.; Proudfoot, A.E.I.; Power, C.A.; Baggiolini, M.; Wells, T.N.C. Functional expression of CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, and CXCR4 chemokine receptors on human platelets. Blood 2000, 96, 4046–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognasse, F.; Laradi, S.; Berthelot, P.; Bourlet, T.; Marotte, H.; Mismetti, P.; Garraud, O.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H. Platelet Inflammatory Response to Stress. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourkarim, R.; Farahpour, M.R.; Rezaei, S.A. Comparison effects of platelet-rich plasma on healing of infected and non-infected excision wounds by the modulation of the expression of inflammatory mediators: Experimental research. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2022, 48, 3339–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orban, Y.; Soliman, M.; Hegab, Y.; Alkilany, M. Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma vs Conventional Dressing in the Management of Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Wounds A Compend. Clin. Res. Pract. 2022, 33, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Liang, J.-X.; Li, S.-H.; Huang, S.; Yan, J.-X.; Xiao, L.-L.; Song, J.-X.; Liu, H.-W. Allogeneic Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy as an Effective and Safe Adjuvant Method for Chronic Wounds. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 246, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, B.M.F.B.; de Oliveira, B.G.R.B.; Bokehi, L.C.; Luiz, R.R.; Carvalho, B.T.F.; Santana, R.F.; de Souza, P.A.; de Paula, G.R.; Teixeira, L.A. Clinical and Microbiological Outcomes Associated with Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Chronic Venous Leg Uclers: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 2021, 48, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Study | Country | Patients (P/C) | Age (P/C) Years | Male (P/C) | Follow-Up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senet et al. [30], 2003 | France | 7/6 | 72.3 (45–88)/72.3 (50–83) | 4/3 | 4 |
| Driver et al. [31], 2006 | America | 19/21 | 58.3 ± 9.7/55.9 ± 8.1 | 16/16 | 3 |
| Anitua et al. [32], 2007 | Spain | 8/7 | 45 ± 20/61 ± 16 | 4/4 | 2 |
| Ahmed et al. [33], 2016 | Egypt | 28/28 | 43.2 ± 18.2/49.8 ± 15.4 | 20/18 | 3 |
| Manuel et al. [34], 2017 | Spain | 55/47 | 65 ± 13.72/69 ± 16.26 | 15/16 | 6 |
| Moneib et al. [35], 2017 | Egypt | 20/20 | 36.4 ± 10.2/32.5 ± 7.5 | 19/20 | 1.5 |
| Elgarhy et al. [36], 2020 | Egypt | 20/20 | 43.70 ± 13.12/43.50 ± 8.10 | 16/16 | 3 |
| Elsaid et al. [37], 2020 | Egypt | 12/12 | 54.7 ± 6.6/55.6 ± 6.5 | 8/6 | 5 |
| Study | Type of Wound | Wound Area (P/C)/cm2 | Treatment Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senet et al. [30], 2003 | Chronic venous ulcers | 13.7 (4.8–27.25)/10.85 (3.7–26.5) | Three times per week until either complete healing or 12 weeks of treatment. |
| Driver et al. [31], 2006 | Diabetic ulcers | 3.4 ± 4.5/3.6 ± 4.0 | Twice a week until the wound healed or a maximum of 12 weeks. |
| Anitua et al. [32], 2007 | Chronic cutaneous ulcers | 5.5 ± 4.8/8.9 ± 8.6 | Until the wound healed or a maximum 8 weeks. |
| Ahmed et al. [33], 2016 | Diabetic ulcers | 6.24 ± 0.77/2.64 ± 0.48 | Wound closure or occurrence of infection or a maximum of 3 months. |
| Manuel et al. [34], 2017 | Venous ulcers | 13.69 ± 30/16.67 ± 23.87 | Saline cleaning once every 3 days and PRP application once a week until the wound healed. |
| Moneib et al. [35], 2017 | Chronic venous leg ulcers | 7.97 ± 16.88/2.94 ± 1.22 | Once per week until the wound healed or a maximum of 6 weeks. |
| Elgarhy et al. [36], 2020 | Chronic venous leg ulcer | 33.70 ± 53.32/15.0 ± 8.30 | PRP application was used weekly until the wound healed or a maximum 3 of months. |
| Elsaid et al. [37], 2020 | Non-healing diabetic foot | - | PRP was used until the wound healed or a maximum of 20 weeks. |
| Study (Year) | Randomization | Concealment of Allocation | Double Blinding | Total Withdrawals and Dropouts | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senet et al. [30], 2003 | * | ** | ** | * | 6 |
| Driver et al. [31], 2006 | ** | ** | ** | * | 7 |
| Anitua et al. [32], 2007 | ** | - | - | * | 3 |
| Ahmed et al. [33], 2016 | * | ** | ** | * | 6 |
| Manuel et al. [34], 2017 | ** | - | - | * | 3 |
| Moneib et al. [35], 2017 | * | - | - | * | 2 |
| Elgarhy et al. [36], 2020 | ** | ** | * | * | 6 |
| Elsaid et al. [37], 2020 | ** | - | - | * | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Xing, F.; Yan, T.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F. The Efficiency and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Dressing in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13030430
Li S, Xing F, Yan T, Zhang S, Chen F. The Efficiency and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Dressing in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(3):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13030430
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shang, Fei Xing, Tongtong Yan, Siya Zhang, and Fengchao Chen. 2023. "The Efficiency and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Dressing in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 3: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13030430
APA StyleLi, S., Xing, F., Yan, T., Zhang, S., & Chen, F. (2023). The Efficiency and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Dressing in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(3), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13030430