Abstract
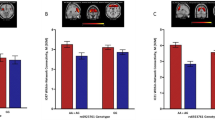
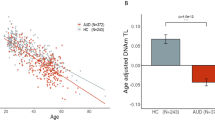
There is growing evidence that disadvantageous influences of the apolipoprotein E4 allele in the central nervous system are modified by environmental and dietary conditions. The present study investigated the gene–environment interaction of apolipoprotein E4 with homocysteine serum levels in patients with alcohol dependence with regard to alcohol-related hippocampal volume loss using volumetric high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. We included 52 patients with alcohol-dependence. ApoE genotypes, homocysteine serum levels and hippocampal volumes were determined. We found a significant impact of homocysteine (F=13.2; df=1; P<0.001; 1−β=0.95), not for ApoE4 genotype (F=0.482; df=1; P=0.49; 1−β=0.05) on hippocampal volume. There was a significant interaction between both factors (ApoE4 × Hcy; F=8.8; df=1; P=0.005; 1−β=0.80). The ApoE4 allele constitutes a risk factor for hippocampal volume loss in patients with alcohol dependence under the conditions of hyperhomocysteinemia. We suggest that the disadvantageous effects of apolipoprotein E4 on alcohol-related brain volume loss are based on certain gene–environment interactions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science 1993; 261: 921–923.
Payami H, Kaye J, Heston LL, Bird TD, Schellenberg GD . Apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 1993; 342: 738.
Poirier J, Davignon J, Bouthillier D, Kogan S, Bertrand P, Gauthier S . Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 1993; 342: 697–699.
Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, George-Hyslop PH, Pericak-Vance MA, Joo SH et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1993; 43: 1467–1472.
Noguchi S, Murakami K, Yamada N . Apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 1993; 342: 737.
Schneider JA, Gearing M, Robbins RS, de l'Aune W, Mirra SS . Apolipoprotein E genotype in diverse neurodegenerative disorders. Ann Neurol 1995; 38: 131–135.
Kalman J, Juhasz A, Majtenyi K, Rimanoczy A, Jakab K, Gardian G et al. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in Pick's disease and in Huntington's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2000; 21: 555–558.
Alberts MJ, Graffagnino C, McClenny C, DeLong D, Strittmatter W, Saunders AM et al. ApoE genotype and survival from intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet 1995; 346: 575.
Friedman G, Froom P, Sazbon L, Grinblatt I, Shochina M, Tsenter J et al. Apolipoprotein E-epsilon4 genotype predicts a poor outcome in survivors of traumatic brain injury. Neurology 1999; 52: 244–248.
Tang MX, Stern Y, Marder K, Bell K, Gurland B, Lantigua R et al. The APOE-epsilon4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer disease among African Americans, whites, and Hispanics. JAMA 1998; 279: 751–755.
Sahota A, Yang M, Gao S, Hui SL, Baiyewu O, Gureje O et al. Apolipoprotein E-associated risk for Alzheimer's disease in the African-American population is genotype dependent. Ann Neurol 1997; 42: 659–661.
Lahiri DK, Sambamurti K, Bennett DA . Apolipoprotein gene and its interaction with the environmentally driven risk factors: molecular, genetic and epidemiological studies of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2004; 25: 651–660.
Osuntokun BO, Sahota A, Ogunniyi AO, Gureje O, Baiyewu O, Adeyinka A et al. Lack of an association between apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 and Alzheimer's disease in elderly Nigerians. Ann Neurol 1995; 38: 463–465.
Sayi JG, Patel NB, Premkumar DR, Adem A, Winblad B, Matuja WB et al. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in elderly east Africans. East Afr Med J 1997; 74: 668–670.
Harper CG, Kril JJ . Neuropathology of alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol 1990; 25: 207–216.
Kril JJ, Homewood J . Neuronal changes in the cerebral cortex of the rat following alcohol treatment and thiamin deficiency. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1993; 52: 586–593.
Lovinger DM, White G, Weight FF . Ethanol inhibits NMDA-activated ion current in hippocampal neurons. Science 1989; 243: 1721–1724.
Tsai G, Gastfriend DR, Coyle JT . The glutamatergic basis of human alcoholism. Am J Psychiatry 1995; 152: 332–340.
Bleich S, Wilhelm J, Graesel E, Degner D, Sperling W, Rössner V et al. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 is associated with hippocampal volume reduction in females with alcoholism. J Neural Transm 2003; 110: 401–411.
Bleich S, Bandelow B, Javaheripour K, Müller A, Degner D, Wilhelm J et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia as a new risk factor for brain shrinkage in patients with alcoholism. Neurosci Lett 2003; 335: 179–182.
Bleich S, Degner D, Wiltfang J, Maler JM, Niedmann P, Cohrs S et al. Elevated homocysteine levels in alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Alcohol 2000; 35: 351–354.
Hultberg B, Berglund M, Andersson A, Frank A . Elevated plasma homocysteine in alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1993; 17: 687–689.
Bleich S, Degner D, Bandelow B, von Ahsen N, Rüther E, Kornhuber J . Plasma homocysteine is a predictor of alcohol withdrawal seizures. Neuroreport 2000; 11: 2749–2752.
Bayerlein K, Hillemacher T, Reulbach U, Mugele B, Sperling W, Kornhuber J et al. Alcoholism-associated hyperhomocysteinemia and previous withdrawal seizures. Biol Psychiatry 2005; 57: 1590–1593.
Wilhelm J, Bayerlein K, Hillemacher T, Reulbach U, Frieling H, Kromolan B et al. Short-term cognition deficits during early alcohol withdrawal are associated with elevated plasma homocysteine levels in patients with alcoholism. J Neural Transm 2006; 113: 357–363.
Fullerton SM, Clark AG, Weiss KM, Nickerson DA, Taylor SL, Stengard JH et al. Apolipoprotein E variation at the sequence haplotype level: implications for the origin and maintenance of a major human polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 67: 881–900.
Zekraoui L, Lagarde JP, Raisonnier A, Gerard N, Aouizerate A, Lucotte G . High frequency of the apolipoprotein E *4 allele in African pygmies and most of the African populations in sub-Saharan Africa. Hum Biol 1997; 69: 575–581.
Corbo RM, Scacchi R . Apolipoprotein E (APOE) allele distribution in the world. Is APOE*4 a ‘thrifty’ allele? Ann Hum Genet 1999; 63 (Part 4): 301–310.
Tang MX, Maestre G, Tsai WY, Liu XH, Feng L, Chung WY et al. Relative risk of Alzheimer disease and age-at-onset distributions, based on APOE genotypes among elderly African Americans, Caucasians, and Hispanics in New York City. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 574–584.
Anello G, Gueant-Rodriguez RM, Bosco P, Gueant JL, Romano A, Namour B et al. Homocysteine and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport 2004; 15: 859–861.
Wetterling T, Veltrup C, Driessen M, John U . Drinking pattern and alcohol-related medical disorders. Alcohol Alcohol 1999; 34: 330–336.
Bjelland I, Tell GS, Vollset SE, Refsum H, Ueland PM . Folate, vitamin B12, homocysteine, and the MTHFR 677C->T polymorphism in anxiety and depression: the Hordaland Homocysteine Study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 618–626.
Frieling H, Römer K, Röschke B, Bönsch D, Wilhelm J, Fiszer R et al. Homocysteine plasma levels are elevated in females with anorexia nervosa. J Neural Transm 2005; 112: 979–985.
Wenham PR, Price WH, Blandell G . Apolipoprotein E genotyping by one-stage PCR. Lancet 1991; 337: 1158–1159.
Ling BL, Dewaele C, Baeyens WR . Application of micro-scale liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection to the determination of thiols. J Chromatogr 1990; 514: 189–198.
Agartz I, Momenan R, Rawlings RR, Kerich MJ, Hommer DW . Hippocampal volume in patients with alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1999; 56: 356–363.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support by a grant (JW, SB) from ELAN fonds (‘Erlanger Leistungsbezogene Anschubfinanzierung und Nachwuchsförderung’), Friedrich-Alexander-University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Duality of Interest
No conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilhelm, J., Frieling, H., von Ahsen, N. et al. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism, homocysteine serum levels and hippocampal volume in patients with alcoholism: an investigation of a gene–environment interaction. Pharmacogenomics J 8, 117–121 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500453
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500453