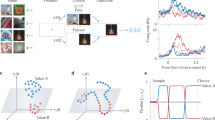
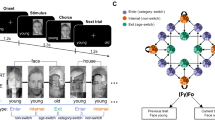
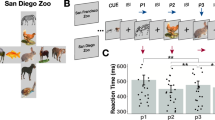
Abstract
The hippocampus and the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) both have important roles in cognitive processes such as learning, memory and decision making. Nevertheless, research on the OFC and hippocampus has proceeded largely independently, and little consideration has been given to the importance of interactions between these structures. Here, evidence is reviewed that the hippocampus and OFC encode parallel, but interactive, cognitive 'maps' that capture complex relationships between cues, actions, outcomes and other features of the environment. A better understanding of the interactions between the OFC and hippocampus is important for understanding the neural bases of flexible, goal-directed decision making.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudebeck, P. H. & Murray, E. A. The orbitofrontal oracle: cortical mechanisms for the prediction and evaluation of specific behavioral outcomes. Neuron 84, 1143–1156 (2014).
Buckner, R. L. The role of the hippocampus in prediction and imagination. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 61, 27–48 (2010).
O'Keefe, J. & Nadel, L. The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map (Clarendon Press, 1978).
Tolman, E. C. Cognitive maps in rats and men. Psychol. Rev. 55, 189–208 (1948).
Tolman, E. C. Purposive Behavior in Animals and Men (Appleton-Century-Crofts, 1932).
Tolman, E. C. & Brunswik, E. The organism and the causal texture of the environment. Psychol. Rev. 42, 43 (1935).
Buzsáki, G. & Moser, E. I. Memory, navigation and theta rhythm in the hippocampal–entorhinal system. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 130–138 (2013).
Eichenbaum, H. & Cohen Neal, J. Can we reconcile the declarative memory and spatial navigation views on hippocampal function? Neuron 83, 764–770 (2014).
Eichenbaum, H., Dudchenko, P., Wood, E., Shapiro, M. & Tanila, H. The hippocampus, memory, and place cells: is it spatial memory or a memory space? Neuron 23, 209–226 (1999).
Wikenheiser, A. M. & Redish, A. D. Decoding the cognitive map: ensemble hippocampal sequences and decision making. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 32, 8–15 (2015).
Dudchenko, P. A. & Wood, E. R. Place fields and the cognitive map. Hippocampus 25, 709–712 (2015).
Redish, A. D. Beyond the Cognitive Map: From Place Cells to Episodic Memory (MIT Press, 1999).
Gallagher, M., McMahan, R. & Schoenbaum, G. Orbitofrontal cortex and representation of incentive value in associative learning. J. Neurosci. 19, 6610–6614 (1999).
Tremblay, L. & Schultz, W. Relative reward preference in primate orbitofrontal cortex. Nature 398, 704–708 (1999).
O'Doherty, J., Kringelbach, M. L., Rolls, E. T., Hornak, J. & Andrews, C. Abstract reward and punishment representations in the human orbitofrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 95–102 (2001).
Gottfried, J. A., O'Doherty, J. & Dolan, R. J. Encoding predictive reward value in human amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex. Science 301, 1104–1107 (2003).
Padoa-Schioppa, C. & Assad, J. A. Neurons in the orbitofrontal cortex encode economic value. Nature 441, 223–226 (2006).
Wallis, J. D. Orbitofrontal cortex and its contribution to decision-making. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 30, 31–56 (2007).
McDannald, M. A., Jones, J. L., Takahashi, Y. K. & Schoenbaum, G. Learning theory: a driving force in understanding orbitofrontal function. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 108, 22–27 (2014).
Thorpe, S., Rolls, E. & Maddison, S. The orbitofrontal cortex: neuronal activity in the behaving monkey. Exp. Brain Res. 49, 93–115 (1983).
Takahashi, Y. K. et al. Expectancy-related changes in firing of dopamine neurons depend on orbitofrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 1590–1597 (2011).
Wilson, R. C., Takahashi, Y. K., Schoenbaum, G. & Niv, Y. Orbitofrontal cortex as a cognitive map of task space. Neuron 81, 267–279 (2014).
Fanselow, M. S. & Dong, H. W. Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 65, 7–19 (2010).
Wallis, J. D. Cross-species studies of orbitofrontal cortex and value-based decision-making. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 13–19 (2012).
Strange, B. A., Witter, M. P., Lein, E. S. & Moser, E. I. Functional organization of the hippocampal longitudinal axis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 15, 655–669 (2014).
Andersen, P., Morris, R., Amaral, D., Bliss, T. & O'Keefe, J. The Hippocampus Book (Oxford Univ. Press, 2006).
Komorowski, R. W., Manns, J. R. & Eichenbaum, H. Robust conjunctive item–place coding by hippocampal neurons parallels learning what happens where. J. Neurosci. 29, 9918–9929 (2009).
Manns, J. R. & Eichenbaum, H. A cognitive map for object memory in the hippocampus. Learn. Mem. 16, 616–624 (2009).
Fenton, A. A. et al. Attention-like modulation of hippocampus place cell discharge. J. Neurosci. 30, 4613–4625 (2010).
Moita, M. A., Rosis, S., Zhou, Y., LeDoux, J. E. & Blair, H. T. Hippocampal place cells acquire location-specific responses to the conditioned stimulus during auditory fear conditioning. Neuron 37, 485–497 (2003).
Larkin, M. C., Lykken, C., Tye, L. D., Wickelgren, J. G. & Frank, L. M. Hippocampal output area CA1 broadcasts a generalized novelty signal during an object–place recognition task. Hippocampus 24, 773–783 (2014).
Lever, C. et al. Environmental novelty elicits a later theta phase of firing in CA1 but not subiculum. Hippocampus 20, 229–234 (2010).
Quirk, G. J., Muller, R. U. & Kubie, J. L. The firing of hippocampal place cells in the dark depends on the rat's recent experience. J. Neurosci. 10, 2008–2017 (1990).
Kennedy, P. J. & Shapiro, M. L. Motivational states activate distinct hippocampal representations to guide goal-directed behaviors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 10805–10810 (2009).
Hollup, S. A., Molden, S., Donnett, J. G., Moser, M.-B. & Moser, E. I. Accumulation of hippocampal place fields at the goal location in an annular watermaze task. J. Neurosci. 21, 1635–1644 (2001).
Hok, V. et al. Goal-related activity in hippocampal place cells. J. Neurosci. 27, 472–482 (2007).
Pfeiffer, B. E. & Foster, D. J. Hippocampal place-cell sequences depict future paths to remembered goals. Nature 497, 74–79 (2013).
Singer, A. C., Carr, M. F., Karlsson, M. P. & Frank, L. M. Hippocampal SWR activity predicts correct decisions during the initial learning of an alternation task. Neuron 77, 1163–1173 (2013).
Dragoi, G. & Tonegawa, S. Preplay of future place cell sequences by hippocampal cellular assemblies. Nature 469, 397–401 (2011).
Ólafsdóttir, H. F., Barry, C., Saleem, A. B., Hassabis, D. & Spiers, H. J. Hippocampal place cells construct reward related sequences through unexplored space. eLife 4, e06063 (2015).
Barron, H. C., Dolan, R. J. & Behrens, T. E. J. Online evaluation of novel choices by simultaneous representation of multiple memories. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 1492–1498 (2013).
Tavares, R. M. et al. A map for social navigation in the human brain. Neuron 87, 231–243 (2015).
Bornstein, A. M. & Daw, N. D. Cortical and hippocampal correlates of deliberation during model-based decisions for rewards in humans. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9, e1003387 (2013).
Bornstein, A. M. & Daw, N. D. Dissociating hippocampal and striatal contributions to sequential prediction learning. Eur. J. Neurosci. 35, 1011–1023 (2012).
Schapiro, A. C., Turk-Browne, N. B., Norman, K. A. & Botvinick, M. M. Statistical learning of temporal community structure in the hippocampus. Hippocampus 26, 3–8 (2015).
Shohamy, D. & Turk-Browne, N. B. Mechanisms for widespread hippocampal involvement in cognition. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 142, 1159 (2013).
Ginther, M. R., Walsh, D. F. & Ramus, S. J. Hippocampal neurons encode different episodes in an overlapping sequence of odors task. J. Neurosci. 31, 2706–2711 (2011).
Allen, T. A., Salz, D. M., McKenzie, S. & Fortin, N. J. Nonspatial sequence coding in CA1 neurons. J. Neurosci. 36, 1547–1563 (2016).
McNaughton, B. L., Barnes, C. A. & O'Keefe, J. The contributions of position, direction, and velocity to single unit activity in the hippocampus of freely-moving rats. Exp. Brain Res. 52, 41–49 (1983).
Stalnaker, T. A., Cooch, N. K. & Schoenbaum, G. What the orbitofrontal cortex does not do. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 620–627 (2015).
Padoa-Schioppa, C. Neurobiology of economic choice: a good-based model. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 34, 333 (2011).
Schoenbaum, G., Roesch, M. R., Stalnaker, T. A. & Takahashi, Y. K. A new perspective on the role of the orbitofrontal cortex in adaptive behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 885–892 (2009).
West, E. A., Forcelli, P. A., McCue, D. L. & Malkova, L. Differential effects of serotonin-specific and excitotoxic lesions of OFC on conditioned reinforcer devaluation and extinction in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 246, 10–14 (2013).
Rhodes, S. E. & Murray, E. A. Differential effects of amygdala, orbital prefrontal cortex, and prelimbic lesions on goal-directed behavior in rhesus macaques. J. Neurosci. 33, 3380–3389 (2013).
Izquierdo, A. D., Suda, R. K. & Murray, E. A. Bilateral orbital prefrontal cortex lesions in rhesus monkeys disrupt choices guided by both reward value and reward contingency. J. Neurosci. 24, 7540–7548 (2004).
Gremel, C. M. & Costa, R. M. Orbitofrontal and striatal circuits dynamically encode the shift between goal-directed and habitual actions. Nat. Commun. 4, 2264 (2013).
Ostlund, S. B. & Balleine, B. W. Orbitofrontal cortex mediates outcome encoding in Pavlovian but not instrumental learning. J. Neurosci. 27, 4819–4825 (2007).
McDannald, M. A., Saddoris, M. P., Gallagher, M. & Holland, P. C. Lesions of orbitofrontal cortex impair rats' differential outcome expectancy learning but not conditioned stimulus-potentiated feeding. J. Neurosci. 25, 4626–4632 (2005).
McDannald, M. A., Lucantonio, F., Burke, K. A., Niv, Y. & Schoenbaum, G. Ventral striatum and orbitofrontal cortex are both required for model-based, but not model-free, reinforcement learning. J. Neurosci. 31, 2700–2705 (2011).
Redish, A. D., Jensen, S., Johnson, A. & Kurth-Nelson, Z. Reconciling reinforcement learning models with behavioral extinction and renewal: Implications for addiction, relapse, and problem gambling. Psychol. Rev. 114, 784–805 (2007).
Sutton, R. S. & Barto, A. G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (MIT Press, 1998).
Gershman, S. J. & Niv, Y. Learning latent structure: carving nature at its joints. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 20, 251–256 (2010).
O'Doherty, J. P., Lee, S. W. & McNamee, D. The structure of reinforcement-learning mechanisms in the human brain. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 1, 94–100 (2015).
Gershman, S. J., Blei, D. & Niv, Y. Context, learning and extinction. Psychol. Rev. 117, 197–209 (2010).
Courville, A. C., Daw, N. D. & Touretzky, D. S. Similarity and discrimination in classical conditioning: a latent variable account. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 17, 313–320 (2005).
Ramus, S. J. & Eichenbaum, H. Neural correlates of olfactory recognition memory in the rat orbitofrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 20, 8199–8208 (2000).
Schoenbaum, G. & Eichenbaum, H. Information coding in the rodent prefrontal cortex. I. Single-neuron activity in orbitofrontal cortex compared with that in piriform cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 74, 733–750 (1995).
Steiner, A. P. & Redish, A. D. Behavioral and neurophysiological correlates of regret in rat decision-making on a neuroeconomic task. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 995–1002 (2014).
Steiner, A. P. & Redish, A. D. The road not taken: neural correlates of decision making in orbitofrontal cortex. Front. Neurosci. 6, 131 (2012).
Abe, H. & Lee, D. Distributed coding of actual and hypothetical outcomes in the orbital and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Neuron 70, 731–741 (2011).
Stalnaker, T. A. et al. Orbitofrontal neurons infer the value and identity of predicted outcomes. Nat. Commun. 5, 3926 (2014).
Tsujimoto, S., Genovesio, A. & Wise, S. P. Monkey orbitofrontal cortex encodes response choices near feedback time. J. Neurosci. 29, 2569–2574 (2009).
Tsujimoto, S. & Sawaguchi, T. Neuronal activity representing temporal prediction of reward in the primate prefrontal cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 93, 3687–3692 (2005).
Bradfield, L. A., Dezfouli, A., van Holstein, M., Chieng, B. & Balleine, B. W. Medial orbitofrontal cortex mediates outcome retrieval in partially observable task situations. Neuron 88, 1268–1280 (2015).
Gläscher, J., Daw, N., Dayan, P. & O'Doherty, J. P. States versus rewards: dissociable neural prediction error signals underlying model-based and model-free reinforcement learning. Neuron 66, 585–595 (2010).
Riceberg, J. S. & Shapiro, M. L. Reward stability determines the contribution of orbitofrontal cortex to adaptive behavior. J. Neurosci. 32, 16402–16409 (2012).
Doll, B. B., Duncan, K. D., Simon, D. A., Shohamy, D. & Daw, N. D. Model-based choices involve prospective neural activity. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 767–772 (2015).
Feierstein, C. E., Quirk, M. C., Uchida, N., Sosulski, D. L. & Mainen, Z. F. Representation of spatial goals in rat orbitofrontal cortex. Neuron 60, 495–507 (2006).
Roesch, M. R., Taylor, A. R. & Schoenbaum, G. Encoding of time-discounted rewards in orbitofrontal cortex is independent of value representation. Neuron 51, 509–520 (2006).
Gupta, A. S., van der Meer, M. A., Touretzky, D. S. & Redish, A. D. Segmentation of spatial experience by hippocampal theta sequences. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 1032–1039 (2012).
Blumenthal, A., Steiner, A., Seeland, K. D. & Redish, A. D. Effects of pharmacological manipulations of NMDA-receptors on deliberation in the multiple-T task. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 95, 376–384 (2011).
Gupta, A. S., van der Meer, M. A., Touretzky, D. S. & Redish, A. D. Hippocampal replay is not a simple function of experience. Neuron 65, 695–705 (2010).
Johnson, A. & Redish, A. D. Neural ensembles in CA3 transiently encode paths forward of the animal at a decision point. J. Neurosci. 27, 12176–12189 (2007).
Tolman, E. C. Prediction of vicarious trial and error by means of the schematic sowbug. Psychol. Rev. 46, 318–336 (1939).
Muenzinger, K. F. Vicarious trial and error at a point of choice: I. A general survey of its relation to learning efficiency. Pedagog. Semin. J. Genet. Psychol. 53, 75–86 (1938).
Redish, A. D. Vicarious trial and error. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 147–159 (2016).
Wikenheiser, A. M. & Redish, A. D. Hippocampal theta sequences reflect current goals. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 289–294 (2015).
Bieri, K. W., Bobbitt, K. N. & Colgin, L. L. Slow and fast gamma rhythms coordinate different spatial coding modes in hippocampal place cells. Neuron 82, 670–681 (2014).
Simon, D. A. & Daw, N. D. Neural correlates of forward planning in a spatial decision task in humans. J. Neurosci. 31, 5526–5539 (2011).
Chadwick, M. J., Jolly, A. E., Amos, D. P., Hassabis, D. & Spiers, H. J. A goal direction signal in the human entorhinal/subicular region. Curr. Biol. 25, 87–92 (2015).
Ferbinteanu, J., Shirvalkar, P. & Shapiro, M. L. Memory modulates journey-dependent coding in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 31, 9135–9146 (2011).
Young, J. J. & Shapiro, M. L. Dynamic coding of goal-directed paths by orbital prefrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 31, 5989–6000 (2011).
Rich, E. L. & Shapiro, M. Rat prefrontal cortical neurons selectively code strategy switches. J. Neurosci. 29, 7208–7219 (2009).
Ferbinteanu, J. & Shapiro, M. L. Prospective and retrospective memory coding in the hippocampus. Neuron 40, 1227–1239 (2003).
Bahar, A. S. & Shapiro, M. L. Remembering to learn: independent place and journey coding mechanisms contribute to memory transfer. J. Neurosci. 32, 2191–2203 (2012).
Shapiro, M. L. & Ferbinteanu, J. Relative spike timing in pairs of hippocampal neurons distinguishes the beginning and end of journeys. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 4287–4292 (2006).
Young, J. J. & Shapiro, M. L. The orbitofrontal cortex and response selection. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1239, 25–32 (2011).
Shapiro, M. L., Riceberg, J. S., Seip-Cammack, K. & Guise, K. G. in Space, Time and Memory in the Hippocampal Formation (eds Derdikman, D. & Knierim, J. J.) 517–560 (Springer, 2014).
Farovik, A. et al. Orbitofrontal cortex encodes memories within value-based schemas and represents contexts that guide memory retrieval. J. Neurosci. 35, 8333–8344 (2015).
McKenzie, S. et al. Hippocampal representation of related and opposing memories develop within distinct, hierarchically organized neural schemas. Neuron 83, 202–215 (2014).
Brogden, W. J. Sensory pre-conditioning. J. Exp. Psychol. 25, 323–332 (1939).
Matsumoto, Y., Hirashima, D. & Mizunami, M. Analysis and modeling of neural processes underlying sensory preconditioning. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 101, 103–113 (2013).
Muller, D., Gerber, B., Hellstern, F., Hammer, M. & Menzel, R. Sensory preconditioning in honeybees. J. Exp. Biol. 203, 1351–1364 (2000).
Port, R. L., Beggs, A. L. & Patterson, M. M. Hippocampal substrate of sensory associations. Physiol. Behav. 39, 643–647 (1987).
Hall, D. & Suboski, M. D. Sensory preconditioning and secord-order conditioning of alarm reactions in zebra danio fish (Brachydanio rerio). J. Comp. Psychol. 109, 76 (1995).
Ward-Robinson, J. et al. Excitotoxic lesions of the hippocampus leave sensory preconditioning intact: implications for models of hippocampal functioning. Behav. Neurosci. 115, 1357–1362 (2001).
Yu, T., Lang, S., Birbaumer, N. & Kotchoubey, B. Neural correlates of sensory preconditioning: a preliminary fMRI investigation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 35, 1297–1304 (2014).
Wimmer, G. E. & Shohamy, D. Preference by association: how memory mechanisms in the hippocampus bias decisions. Science 338, 270–273 (2012).
Karn, H. W. Sensory pre-conditioning and incidental learning in human subjects. J. Exp. Psychol. 37, 540 (1947).
Kojima, S. et al. Sensory preconditioning for feeding response in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. Brain Res. 808, 113–115 (1998).
Port, R. L. & Patterson, M. M. Fimbrial lesions and sensory preconditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 98, 584 (1984).
Rescorla, R. A. & Cunningham, C. L. Within-compound flavor associations. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process 4, 267–275 (1978).
Nicholson, D. A. & Freeman Jr, J. H. Lesions of the perirhinal cortex impair sensory preconditioning in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 112, 69–75 (2000).
Robinson, S., Keene, C. S., Iaccarino, H. F., Duan, D. & Bucci, D. J. Involvement of retrosplenial cortex in forming associations between multiple sensory stimuli. Behav. Neurosci. 125, 578 (2011).
Robinson, S. et al. Chemogenetic silencing of neurons in retrosplenial cortex disrupts sensory preconditioning. J. Neurosci. 34, 10982–10988 (2014).
Jones, J. L. et al. Orbitofrontal cortex supports behavior and learning using inferred but not cached values. Science 338, 953–956 (2012).
Abela, A. R. & Chudasama, Y. Dissociable contributions of the ventral hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex to decision-making with a delayed or uncertain outcome. Eur. J. Neurosci. 37, 640–647 (2013).
Mariano, T. Y. et al. Impulsive choice in hippocampal but not orbitofrontal cortex-lesioned rats on a nonspatial decision-making maze task. Eur. J. Neurosci. 30, 472–484 (2009).
Cheung, T. H. C. & Cardinal, R. N. Hippocampal lesions facilitate instrumental learning with delayed reinforcement but induce impulsive choice in rats. BMC Neurosci. 6, 36 (2005).
Bett, D., Murdoch, L. H., Wood, E. R. & Dudchenko, P. A. Hippocampus, delay discounting, and vicarious trial-and-error. Hippocampus 25, 643–654 (2015).
O'Doherty, J. et al. Sensory-specific satiety-related olfactory activation of the human orbitofrontal cortex. Neuroreport 11, 399–403 (2000).
West, E. A., DesJardin, J. T., Gale, K. & Malkova, L. Transient inactivation of orbitofrontal cortex blocks reinforcer devaluation in macaques. J. Neurosci. 31, 15128–15135 (2011).
Schoenbaum, G. & Roesch, M. Orbitofrontal cortex, associative learning, and expectancies. Neuron 47, 633–636 (2005).
Higgs, S., Williamson, A. C., Rotshtein, P. & Humphreys, G. W. Sensory-specific satiety is intact in amnesics who eat multiple meals. Psychol. Sci. 19, 623–628 (2008).
Corbit, L. H., Ostlund, S. B. & Balleine, B. W. Sensitivity to instrumental contingency degradation is mediated by the entorhinal cortex and its efferents via the dorsal hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 22, 10976–10984 (2002).
Corbit, L. H. & Balleine, B. W. The role of the hippocampus in instrumental conditioning. J. Neurosci. 20, 4233–4239 (2000).
Chudasama, Y., Wright, K. S. & Murray, E. A. Hippocampal lesions in rhesus monkeys disrupt emotional responses but not reinforcer devaluation effects. Biol. Psychiatry 63, 1084–1091 (2008).
Machado, C. J. & Bachevalier, J. The impact of selective amygdala, orbital frontal cortex, or hippocampal formation lesions on established social relationships in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Behav. Neurosci. 120, 761 (2006).
Reichelt, A. C., Lin, T. E., Harrison, J. J., Honey, R. C. & Good, M. A. Differential role of the hippocampus in response-outcome and context-outcome learning: evidence from selective satiation procedures. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 96, 248–253 (2011).
Carr, M. F., Jadhav, S. P. & Frank, L. M. Hippocampal replay in the awake state: a potential substrate for memory consolidation and retrieval. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 147–153 (2011).
Malhotra, S., Cross, R. W. & van der Meer, M. A. Theta phase precession beyond the hippocampus. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 39–65 (2012).
van der Meer, M., Kurth-Nelson, Z. & Redish, A. D. Information processing in decision-making systems. Neuroscientist 18, 342–359 (2012).
Johnson, A., van der Meer, M. A. & Redish, A. D. Integrating hippocampus and striatum in decision-making. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 17, 692–697 (2007).
Kurth-Nelson, Z., Bickel, W. & Redish, A. D. A theoretical account of cognitive effects in delay discounting. Eur. J. Neurosci. 35, 1052–1064 (2012).
Rolls, E., Sienkiewicz, Z. & Yaxley, S. Hunger modulates the responses to gustatory stimuli of single neurons in the caudolateral orbitofrontal cortex of the macaque monkey. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1, 53–60 (1989).
Rolls, E. T. The functions of the orbitofrontal cortex. Brain Cogn. 55, 11–29 (2004).
Pearson, J. M., Watson, K. K. & Platt, M. L. Decision making: the neuroethological turn. Neuron 82, 950–965 (2014).
Watson, K. K. & Platt, M. L. Social signals in primate orbitofrontal cortex. Curr. Biol. 22, 2268–2273 (2012).
Ross, R., LoPresti, M., Schon, K. & Stern, C. Role of the hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex during the disambiguation of social cues in working memory. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 13, 900–915 (2013).
Eichenbaum, H. Memory on time. Trends Cogn. Sci. 17, 81–88 (2013).
Eichenbaum, H. Time cells in the hippocampus: a new dimension for mapping memories. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 15, 732–744 (2014).
MacDonald, C. J., Lepage, K. Q., Eden, U. T. & Eichenbaum, H. Hippocampal “time cells” bridge the gap in memory for discontiguous events. Neuron 71, 737–749 (2011).
Johnson, A. & Crowe, D. Revisiting Tolman: theories and cognitive maps. Cognitive Critique 1, 43–72 (2009).
Tolman, E. C. There is more than one kind of learning. Psychol. Rev. 56, 144 (1949).
Tolman, E. C. The determiners of behavior at a choice point. Psychol. Rev. 45, 1–41 (1938).
Tolman, E. C., Ritchie, B. F. & Kalish, D. Studies in spatial learning. I. Orientation and the short-cut. J. Exp. Psychol. 36, 13–24 (1946).
Tolman, E. C., Ritchie, B. F. & Kalish, D. Studies in spatial learning. II. Place learning versus response learning. J. Exp. Psychol. 36, 221–229 (1946).
Schiller, D. et al. Memory and space: towards an understanding of the cognitive map. J. Neurosci. 35, 13904–13911 (2015).
Rescorla, R. A. & Wagner, A. R. in Classical Conditioning II: Current Research and Theory (eds Black, A. H. & Prokasy, W. F.) 64–99 (Appleton-Century-Crofts, 1972).
Pearce, J. M. & Hall, G. A model for Pavlovian learning: variations in the effectiveness of conditioned but not of unconditioned stimuli. Psychol. Rev. 87, 532–552 (1980).
Mackintosh, N. J. A theory of attention: variations in the associability of stimuli with reinforcement. Psychol. Rev. 82, 276–298 (1975).
Doll, B. B., Shohamy, D. & Daw, N. D. Multiple memory systems as substrates for multiple decision systems. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 117, 4–13 (2015).
Dayan, P. & Daw, N. D. Decision theory, reinforcement learning, and the brain. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 8, 429–453 (2008).
Balleine, B. W., Daw, N. D. & O'Doherty, J. P. in Neuroeconomics: Decision Making and the Brain (eds Glimcher, P. W. & Fehr, E.) 367–385 (Academic Press, 2008).
Daw, N. D., Niv, Y. & Dayan, P. Uncertainty-based competition between prefrontal and dorsolateral striatal systems for behavioral control. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1704–1711 (2005).
Jay, T. M. & Witter, M. P. Distribution of hippocampal CA1 and subicular efferents in the prefrontal cortex of the rat studied by means of anterograde transport of Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin. J. Comp. Neurol. 313, 574–586 (1991).
Barbas, H. & Blatt, G. J. Topographically specific hippocampal projections target functionally distinct prefrontal areas in the rhesus monkey. Hippocampus 5, 511–533 (1995).
Insausti, R. & Munoz, M. Cortical projections of the non-entorhinal hippocampal formation in the cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis). Eur. J. Neurosci. 14, 435–451 (2001).
Aggleton, J. P. & Christiansen, K. The subiculum: the heart of the extended hippocampal system. Prog. Brain Res. 219, 65–82 (2015).
Prasad, J. A. & Chudasama, Y. Viral tracing identifies parallel disynaptic pathways to the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 33, 8494–8503 (2013).
McKenna, J. T. & Vertes, R. P. Afferent projections to nucleus reuniens of the thalamus. J. Comp. Neurol. 480, 115–142 (2004).
Vertes, R. P., Hoover, W. B., Szigeti-Buck, K. & Leranth, C. Nucleus reuniens of the midline thalamus: link between the medial prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus. Brain Res. Bull. 71, 601–609 (2007).
Griffin, A. L. Role of the thalamic nucleus reuniens in mediating interactions between the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex during spatial working memory. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 9, 29 (2015).
Varela, C., Kumar, S., Yang, J. Y. & Wilson, M. A. Anatomical substrates for direct interactions between hippocampus, medial prefrontal cortex, and the thalamic nucleus reuniens. Brain Struct. Funct. 219, 911–929 (2014).
Mitchell, A. S. et al. Advances in understanding mechanisms of thalamic relays in cognition and behavior. J. Neurosci. 34, 15340–15346 (2014).
Witter, M. P. et al. Cortico-hippocampal communication by way of parallel parahippocampal-subicular pathways. Hippocampus 10, 398–410 (2000).
Schultz, W., Dayan, P. & Montague, R. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275, 1593–1599 (1997).
Jo, Y. S. & Mizumori, S. J. Y. Prefrontal regulation of neuronal activity in the ventral tegmental area. Cereb. Cortex http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv215 (2015).
Luo, A. H., Tahsili-Fahadan, P., Wise, R. A., Lupica, C. R. & Aston-Jones, G. Linking context with reward: a functional circuit from hippocampal CA3 to ventral tegmental area. Science 333, 353–357 (2011).
Fujisawa, S. & Buzsáki, G. A. 4 Hz oscillation adaptively synchronizes prefrontal, VTA, and hippocampal activities. Neuron 72, 153–165 (2011).
Groenewegen, H. J., Wright, C. I. & Beijer, A. V. J. in The Emotional Motor System (eds Holstege, G., Bandler, R. & Saper, C. B.) 485–512 (Elsevier, 1996).
Mogenson, G. J., Jones, D. L. & Yim, C. Y. From motivation to action: Functional interface between the limbic system and the motor system. Prog. Neurobiol. 14, 69–97 (1980).
van der Meer, M. A. & Redish, A. D. Expectancies in decision making, reinforcement learning, and ventral striatum. Front. Neurosci. 4, 6 (2010).
Lavoie, A. M. & Mizumori, S. J. Y. Spatial-, movement- and reward-sensitive discharge by medial ventral striatum neurons in rats. Brain Res. 638, 157–168 (1994).
van der Meer, M. A & Redish, A. D. Covert expectation-of-reward in rat ventral striatum at decision points. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 3, 1–15 (2009).
Miyazaki, K., Miwazaki, K. W. & Matsumoto, G. Different representation of forthcoming reward in nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex. Neuroreport 15, 721–726 (2003).
van der Meer, M. A. A. & Redish, A. D. Theta phase precession in rat ventral striatum links place and reward information. J. Neurosci. 31, 2843–2854 (2011).
Cooch, N. K. et al. Orbitofrontal lesions eliminate signalling of biological significance in cue-responsive ventral striatal neurons. Nat. Commun. 6, 7195 (2015).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank members of the Schoenbaum laboratory for helpful discussions on the topics addressed here and for feedback on earlier versions of this manuscript. This work was supported by funding from the US National Institute on Drug Abuse at the Intramural Research Program. The opinions expressed in this article are the authors' own and do not reflect the view of the US National Institutes of Health, the US Department of Health and Human Services or the US government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
PowerPoint slides
Glossary
- Economic value
-
An integrative measure of how good an outcome is to a decision maker that distils the many multidimensional features of that outcome into a unidimensional measure of worth.
- Outcome devaluation
-
The process of rendering a normally appetitive outcome aversive, typically by pairing it with illness.
- Place cells
-
Pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus that fire action potentials when an animal occupies or passes through particular portions of the environment.
- Reinforcement-learning models
-
A collection of machine-learning models that are inspired by psychological learning theory and that are aimed at solving the problem of using experience of the world to guide future behaviour.
- Representational similarity analysis
-
An analysis approach that quantifies the similarity (or dissimilarity) of neural ensemble representations evoked by different conditions.
- Response inhibition
-
The active suppression of actions that are not adaptive in the current setting.
- Specific satiety
-
A means of devaluing a particular outcome by allowing an animal unrestricted access to it before a test session.
- Stimulus–stimulus associations
-
Associations that are formed between neutral stimuli in the environment in the absence of explicit reinforcement.
- Vicarious trial and error
-
(VTE). A pause and orient pattern of behaviour that decision makers often show when deliberating over potential choices. This is thought to be an overt marker of covert, mental processes that simulate potential outcomes of each course of action.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wikenheiser, A., Schoenbaum, G. Over the river, through the woods: cognitive maps in the hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 17, 513–523 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.56
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.56