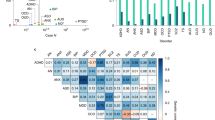
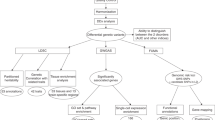
Abstract
Recent genomic studies have revealed the highly polygenic nature of psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. Many of the individual genetic associations are shared across multiple disorders in a way that points to extensive biological pleiotropy and further challenges the biological validity of existing diagnostic approaches. Here we argue that the existence of risk alleles specific to a single diagnostic category is unlikely. We also highlight some of the important clinical repercussions of pleiotropy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whiteford, H.A. et al. Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 382, 1575–1586 (2013).
Salomon, J.A. et al. Common values in assessing health outcomes from disease and injury: disability weights measurement study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380, 2129–2143 (2012).
Owen, M.J. New approaches to psychiatric diagnostic classification. Neuron 84, 564–571 (2014).
Malaspina, D. et al. Schizoaffective disorder in the DSM-5. Schizophr. Res. 150, 21–25 (2013).
van Os, J. & Kapur, S. Schizophrenia. Lancet 374, 635–645 (2009).
Lichtenstein, P. et al. Common genetic determinants of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in Swedish families: a population-based study. Lancet 373, 234–239 (2009).
Kapur, S., Phillips, A.G. & Insel, T.R. Why has it taken so long for biological psychiatry to develop clinical tests and what to do about it? Mol. Psychiatry 17, 1174–1179 (2012).
Linden, D.E. The challenges and promise of neuroimaging in psychiatry. Neuron 73, 8–22 (2012).
Sanders, S.J. et al. Insights into autism spectrum disorder genomic architecture and biology from 71 risk loci. Neuron 87, 1215–1233 (2015).
Gaugler, T. et al. Most genetic risk for autism resides with common variation. Nat. Genet. 46, 881–885 (2014).
Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature 511, 421–427 (2014).
Rees, E. et al. Analysis of copy number variations at 15 schizophrenia-associated loci. Br. J. Psychiatry 204, 108–114 (2014).
Fromer, M. et al. De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks. Nature 506, 179–184 (2014).
Purcell, S.M. et al. A polygenic burden of rare disruptive mutations in schizophrenia. Nature 506, 185–190 (2014).
Singh, T. et al. Rare loss-of-function variants in SETD1A are associated with schizophrenia and developmental disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 571–577 (2016).
Green, E.K. et al. Copy number variation in bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 21, 89–93 (2016).
Hyde, C.L. et al. Identification of 15 genetic loci associated with risk of major depression in individuals of European descent. Nat. Genet. 48, 1031–1036 (2016).
Paaby, A.B. & Rockman, M.V. The many faces of pleiotropy. Trends Genet. 29, 66–73 (2013).
Solovieff, N., Cotsapas, C., Lee, P.H., Purcell, S.M. & Smoller, J.W. Pleiotropy in complex traits: challenges and strategies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 483–495 (2013).
Kirov, G. et al. The penetrance of copy number variations for schizophrenia and developmental delay. Biol. Psychiatry 75, 378–385 (2014).
Rees, E. et al. Analysis of intellectual disability copy number variants for association with schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry 73, 963–969 (2016).
Rujescu, D. et al. Disruption of the neurexin 1 gene is associated with schizophrenia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 988–996 (2009).
Deciphering Developmental Disorders Study. Large-scale discovery of novel genetic causes of developmental disorders. Nature 519, 223–228 (2015).
The International Schizophrenia Consortium. Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 460, 748–752 (2009).
Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs. Nat. Genet. 45, 984–994 (2013).
Bulik-Sullivan, B. et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 47, 1236–1241 (2015).
Hamshere, M.L. et al. Shared polygenic contribution between childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and adult schizophrenia. Br. J. Psychiatry 203, 107–111 (2013).
Samocha, K.E. et al. A framework for the interpretation of de novo mutation in human disease. Nat. Genet. 46, 944–950 (2014).
Kirov, G. et al. De novo CNV analysis implicates specific abnormalities of postsynaptic signalling complexes in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 17, 142–153 (2012).
Niarchou, M. et al. Psychopathology and cognition in children with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Br. J. Psychiatry 204, 46–54 (2014).
Stefansson, H. et al. CNVs conferring risk of autism or schizophrenia affect cognition in controls. Nature 505, 361–366 (2014).
Tansey, K.E. et al. Common alleles contribute to schizophrenia in CNV carriers. Mol. Psychiatr. 21, 1085–1089 (2015).
Rees, E. et al. Evidence that duplications of 22q11.2 protect against schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 19, 37–40 (2014).
Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs. Nat. Genet. 45, 984–994 (2012).
Costain, G. et al. Pathogenic rare copy number variants in community-based schizophrenia suggest a potential role for clinical microarrays. Hum. Mol. Genet. 22, 4485–4501 (2013).
Gershon, E.S. & Alliey-Rodriguez, N. New ethical issues for genetic counseling in common mental disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 170, 968–976 (2013).
Walters, J.T.R. & Owen, M.J. Endophenotypes in psychiatric genetics. Mol. Psychiatry 12, 886–890 (2007).
Kendler, K.S. & Neale, M.C. Endophenotype: a conceptual analysis. Mol. Psychiatr 15, 789–797 (2010).
Antilla, V. et al. Analysis of shared heritability in common disorders of the brain. Preprint at bioRxiv http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/048991 (2016).
Ruderfer, D.M. et al. A family-based study of common polygenic variation and risk of schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 16, 887–888 (2011).
Hamshere, M.L. et al. Genome-wide significant associations in schizophrenia to ITIH3/4, CACNA1C and SDCCAG8, and extensive replication of associations reported by the Schizophrenia PGC. Mol. Psychiatry 18, 708–712 (2013).
Flint, J., Timpson, N. & Munafò, M. Assessing the utility of intermediate phenotypes for genetic mapping of psychiatric disease. Trends Neurosci. 37, 733–741 (2014).
Franke, B. et al. Genetic influences on schizophrenia and subcortical brain volumes: large-scale proof of concept. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 420–431 (2016).
Cuthbert, B.N. The RDoC framework: facilitating transition from ICD/DSM to dimensional approaches that integrate neuroscience and psychopathology. World Psychiatry 13, 28–35 (2014).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Medical Research Council (MRC) Centre grant MR/L010305/1 and program grant G0800509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Michael C.O'Donovan has received a consultancy fee from Roche for participation in a discussion about using genetics to identify drug targets.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Donovan, M., Owen, M. The implications of the shared genetics of psychiatric disorders. Nat Med 22, 1214–1219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4196
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4196
This article is cited by
-
A shared neural basis underlying psychiatric comorbidity
Nature Medicine (2023)
-
Schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorders and developmental disorders share specific disruptive coding mutations
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Genetic variants in the bipolar disorder risk locus SYNE1 that affect CPG2 expression and protein function
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Bivariate genome-wide association analyses of the broad depression phenotype combined with major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder or schizophrenia reveal eight novel genetic loci for depression
Molecular Psychiatry (2020)
-
The pathophysiological impact of stress on the dopamine system is dependent on the state of the critical period of vulnerability
Molecular Psychiatry (2020)