Abstract
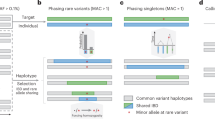
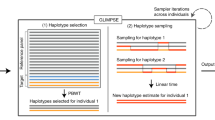
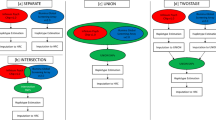
The 1000 Genomes Project and disease-specific sequencing efforts are producing large collections of haplotypes that can be used as reference panels for genotype imputation in genome-wide association studies (GWAS). However, imputing from large reference panels with existing methods imposes a high computational burden. We introduce a strategy called 'pre-phasing' that maintains the accuracy of leading methods while reducing computational costs. We first statistically estimate the haplotypes for each individual within the GWAS sample (pre-phasing) and then impute missing genotypes into these estimated haplotypes. This reduces the computational cost because (i) the GWAS samples must be phased only once, whereas standard methods would implicitly repeat phasing with each reference panel update, and (ii) it is much faster to match a phased GWAS haplotype to one reference haplotype than to match two unphased GWAS genotypes to a pair of reference haplotypes. We implemented our approach in the MaCH and IMPUTE2 frameworks, and we tested it on data sets from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (WTCCC2), the Genetic Association Information Network (GAIN), the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) and the 1000 Genomes Project. This strategy will be particularly valuable for repeated imputation as reference panels evolve.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
International HapMap Consortium. The International HapMap Project. Nature 426, 789–796 (2003).
Altshuler, D.M. et al. Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature 467, 52–58 (2010).
1000 Genomes Project Consortium. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 467, 1061–1073 (2010).
Marchini, J. & Howie, B. Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11, 499–511 (2010).
Li, Y., Willer, C., Sanna, S. & Abecasis, G. Genotype imputation. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 10, 387–406 (2009).
Howie, B.N., Donnelly, P. & Marchini, J. A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 5, e1000529 (2009).
Burdick, J.T., Chen, W.M., Abecasis, G.R. & Cheung, V.G. In silico method for inferring genotypes in pedigrees. Nat. Genet. 38, 1002–1004 (2006).
Chen, W.M. & Abecasis, G.R. Family-based association tests for genomewide association scans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 913–926 (2007).
Kong, A. et al. Detection of sharing by descent, long-range phasing and haplotype imputation. Nat. Genet. 40, 1068–1075 (2008).
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447, 661–678 (2007).
Marchini, J., Howie, B., Myers, S., McVean, G. & Donnelly, P. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 39, 906–913 (2007).
Li, Y., Willer, C.J., Ding, J., Scheet, P. & Abecasis, G.R. MaCH: using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes. Genet. Epidemiol. 34, 816–834 (2010).
Varilo, T. & Peltonen, L. Isolates and their potential use in complex gene mapping efforts. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 14, 316–323 (2004).
Peltonen, L., Palotie, A. & Lange, K. Use of population isolates for mapping complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 1, 182–190 (2000).
Scott, L.J. et al. A genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science 316, 1341–1345 (2007).
Marchini, J. et al. A comparison of phasing algorithms for trios and unrelated individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78, 437–450 (2006).
Delaneau, O., Marchini, J. & Zagury, J.F. A linear complexity phasing method for thousands of genomes. Nat. Methods 9, 179–181 (2012).
Manolio, T.A. et al. New models of collaboration in genome-wide association studies: the Genetic Association Information Network. Nat. Genet. 39, 1045–1051 (2007).
Women's Health Initiative Study Group. Design of the Women's Health Initiative clinical trial and observational study. The Women's Health Initiative Study Group. Control. Clin. Trials 19, 61–109 (1998).
Abecasis, G.R. & Wigginton, J.E. Handling marker-marker linkage disequilibrium: pedigree analysis with clustered markers. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 77, 754–767 (2005).
Nair, R.P. et al. Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-κB pathways. Nat. Genet. 41, 199–204 (2009).
Stephens, M. & Donnelly, P. A comparison of bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population genotype data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73, 1162–1169 (2003).
Scheet, P. & Stephens, M. A fast and flexible statistical model for large-scale population genotype data: applications to inferring missing genotypes and haplotypic phase. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78, 629–644 (2006).
Baum, L.E., Petrie, T., Soules, G. & Weiss, N. A maximization technique occurring in statistical analysis of probabilistic functions of Markov chains. Ann. Math. Statist. 41, 164–171 (1970).
Browning, B.L. & Browning, S.R. A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype-phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 84, 210–223 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Boehnke for critical reading, advice and suggestion, Y. Li for aid with cleaning the WHI data and the two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. B.H. and M.S. were supported by a grant from the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI; HGO2585) to M.S. J.M. was supported by a grant from the UK Medical Research Council (G0801823). C.F. and G.R.A. were supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH; DK0855840, HG005552 and HG005581). This study makes use of data generated by the WTCCC, GAIN and WHI. A full list of the investigators who contributed to the generation of the WTCCC data is available from the WTCCC web site (see URLs). The WTCCC was partially funded by the Wellcome Trust under awards 076113 and 085475. For details of contributors to the GAIN and WHI studies, please see the corresponding dbGaP accessions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.H., C.F., M.S., J.M. and G.R.A. designed the methods and experiments. B.H. and C.F. ran the experiments and wrote the first draft; all authors contributed critical reviews of the manuscript during its preparation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Note, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Figures 1–4 (PDF 465 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howie, B., Fuchsberger, C., Stephens, M. et al. Fast and accurate genotype imputation in genome-wide association studies through pre-phasing. Nat Genet 44, 955–959 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2354
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2354