Summary
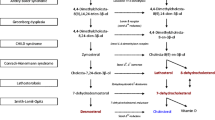
A sensitive, reliable, and easily performed procedure is described for the prenatal and postnatal detection of inborn errors of propionate, methylmalonate, and cobalamin metabolism using cultured amniotic cells and skin fibroblasts. With this assay, control fibroblast lines incorporated a mean of 6.89 nanoatoms 14C/mg protein from [1-14C]propionate into trichloroacetic acid (TCA)-precipitable cell material in 10h. Twenty-five mutant fibroblast lines from patients with propionicacidemia or one of the methylmalonicacidemias fixed 0.04 to 0.93 nanoatoms 14C/mg. Considerable variation was observed, both among and within discrete mutant classes, with respect to the residual amount of propionate pathway activity, possibly reflecting further molecular heterogeneity in these disorders.
We applied this procedure to cultured amniotic cells from controls and 4 midtrimester pregnancies at risk for methylmalonicacidemia and diagnosed one fetus with a methylmalonyl CoA apomutase defect and 3 fetuses which were unaffected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böhlen, P., Stein, S., Dairman, W., Udenfriend, S.: Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 155, 213–220 (1973)
Gravel, R. A., Mahoney, M. J., Ruddle, F. H., Rosenberg, L. E.: Genetic complementation in heterokaryons of human fibroblasts defective in cobalamin metabolism. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 72, 3181–3185 (1975)
Hill, H. Z., Puck, T. T.: Detection of inborn errors of metabolism: galactosemia. Science 179, 1136–1139 (1973)
Hill, H. Z., Goodman, S. I.: Detection of inborn errors of metabolism. II. Defects in propionic acid metabolism. Clin. Genet. 6, 73–78 (1974a)
Hill, H. Z., Goodman, S. I.: Detection of inborn errors of metabolism. III. Defects in urea cycle metabolism. Clin. Genet. 6, 79–81 (1974b)
Hill, H. Z.: The effect of pH on incorporation of galactose by a normal human cell line and cell lines from patients with defective galactose metabolism. J. Cell. Physiol. 87, 313–320 (1976)
Mahoney, M. J., Hart, A. C., Steen, V. D., Rosenberg, L. E.: Methylmalonicacidemia: biochemical heterogeneity in defects of 5′-deoxyadenosylcobalamin synthesis. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 72, 2799–2803 (1975a)
Mahoney, M. J., Rosenberg, L. E., Lindblad, B., Waldenstrom, J., Zetterstrom, R.: Prenatal diagnosis of methylmalonic aciduria. Acta paediat. scand. 64, 44–48 (1975b)
Morrow, G., III, Barness, L. A., Cardinale, G. J., Abeles, R. H., Flaks, J. G.: Congenital methylmalonic acidemia: enzymatic evidence for two forms of the disease. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 63, 191–197 (1969)
Morrow, G., III, Revsin, B., Mathews, C., Giles, H.: A simple, rapid method for prenatal detection of defects in propionate metabolism. Clin. Genet. (in press, 1976)
Rosenberg, L. E.: Disorders of propionate, methylmalonate, and vitamin B12 metabolism. In: The metabolic basis of inherited disease, 3rd ed., J. B. Stanbury, J. B. Wyngaarden, D. S. Fredrickson, eds., pp. 440–458. New York: McGraw-Hill 1972
Rosenberg, L. E.: Vitamin-responsive inherited metabolic disorders. In: Advances in human genetics, Vol. 6, H. Harris, K. Hirschhorn, eds., pp. 1–74. New York: Plenum 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willard, H.F., Ambani, L.M., Hart, A.C. et al. Rapid prenatal and postnatal detection of inborn errors of propionate, methylmalonate, and cobalamin metabolism: A sensitive assay using cultured cells. Hum Genet 34, 277–283 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295291
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295291