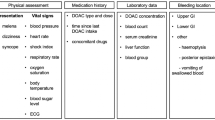
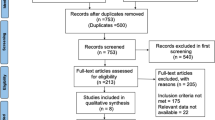
Abstract
Older adults, the fastest growing population, represent almost 50% of all users of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). Unfortunately, we have very little relevant pharmacological and clinical data on DOACs, especially in older adults with geriatric profiles. This is highly relevant as pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) often differ substantially in this population. Hence, we need to obtain a better understanding of the PK/PD of DOACs in older adults, to ensure appropriate treatment. This review summarises the current insights into PK/PD of DOACs in older adults. A search was undertaken up to October 2022 to identify PK/PD studies of apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban, that included older adults aged ≥ 75 years. This review identified 44 articles. Older age alone did not influence exposure of edoxaban, rivaroxaban and dabigatran, while apixaban peak concentrations were 40% higher in older adults than in young volunteers. Nevertheless, high interindividual variability in DOAC exposure in older adults was noted, which can be explained by distinctive older patient characteristics, such as kidney function, changes in body composition (especially reduced muscle mass), and co-medication with P-gp inhibitors, which is in line with the current dosing reduction criteria of apixaban, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban. Dabigatran had the largest interindividual variability among all DOACs since its dose adjustment criterion is only age, and thus it is not a preferable option. Additionally, DOAC exposure, which fell outside of on-therapy ranges, was significantly related to stroke and bleeding events. No definite thresholds linked to these outcomes in older adults have been established.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vos T, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–59.
Wilke T, Groth A, Mueller S, Pfannkuche M, Verheyen F, Linder R, et al. Incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation: an analysis based on 8.3 million patients. Europace. 2013;15(4):486–93.
Wilkinson C, Clegg A, Todd O, Rockwood K, Yadegarfar ME, Gale CP, et al. Atrial fibrillation and oral anticoagulation in older people with frailty: a nationwide primary care electronic health records cohort study. Age Ageing. 2021;50(3):772–9.
Laupacis A, et al. Risk factors for stroke and efficacy of antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation Analysis of pooled data from five randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154(13):1449–57.
Hart RG, Pearce LA, Aguilar MI. Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146(12):857–67.
Singer DE, Chang Y, Fang MC, Borowsky LH, Pomernacki NK, Udaltsova N, et al. The net clinical benefit of warfarin anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(5):297–305.
Steffel J, Collins R, Antz M, Cornu P, Desteghe L, Haeusler KG, et al. 2021 European heart rhythm association practical guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. EP Europace. 2021;23(10):1612–76.
Granger CB, Alexander JH, Mcmurray JJV, Lopes RD, Hylek EM, Hanna M, et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(11):981–92.
Giugliano RP, Ruff CT, Braunwald E, Murphy SA, Wiviott SD, Halperin JL, et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(22):2093–104.
Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, Eikelboom J, Oldgren J, Parekh A, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139–51.
Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J, Pan G, Singer DE, Hacke W, et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(10):883–91.
Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, Crowther M, Hylek EM, Palareti G. Oral anticoagulant therapy. Chest. 2012;141(2):e44S-e88S.
Witt DM, Clark NP, Kaatz S, Schnurr T, Ansell JE. Guidance for the practical management of warfarin therapy in the treatment of venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2016;41(1):187–205.
De Groot JR, Weiss TW, Kelly P, Monteiro P, Deharo JC, De Asmundis C, et al. Edoxaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation in routine clinical care: 1-year follow-up of the prospective observational ETNA-AF-Europe study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2021;7(FI1):f30–9.
Proietti M, Romanazzi I, Romiti GF, Farcomeni A, Lip GYH. Real-world use of apixaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Stroke. 2018;49(1):98–106.
Ibáñez L, Sabaté M, Vidal X, Ballarin E, Rottenkolber M, Schmiedl S, et al. Incidence of direct oral anticoagulant use in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and characteristics of users in 6 European countries (2008–2015): a cross-national drug utilization study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;85(11):2524–39.
Hias J, Van der Linden L, Walgraeve K, Gijsen M, Mian P, Koch BCP, et al. Pharmacokinetics of 2 oral paracetamol formulations in hospitalized octogenarians. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;88:1020–30.
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2009 update. Circulation. 2009;119(3):e21–181.
Eurostat. Ageing Europe: Looking at the lives of older people in the EU. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. 2019.
Bramer WM, Giustini D, De Jonge GB, Holland L, Bekhuis T. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. J Med Libr Assoc. 2016;104(3):240–3.
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:1.
Bendayan M, Mardigyan V, Williamson D, Chen-Tournoux A, Eintracht S, Rudski L, et al. Muscle mass and direct oral anticoagulant activity in older adults with atrial fibrillation. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(4):1012–8.
Bernier M, Lancrerot SL, Rocher F, Van-Obberghen EK, Olivier P, Lavrut T, et al. Major bleeding events in octagenarians associated with drug interactions between dabigatran and P-gp inhibitors. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2019;16(11):806–11.
Bhagirath VC, Chan N, Hirsh J, Ginsberg J, de Vries TAC, Eikelboom J. Plasma apixaban levels in patients treated off label with the lower dose. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(24):2906–7.
Chaussade E, Hanon O, Boully C, Labourée F, Caillard L, Gerotziafas G, et al. Real-life peak and trough dabigatran plasma measurements over time in hospitalized geriatric patients with atrial fibrillation. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22(1):165–73.
Comans AL, Sennesael AL, Bihin B, Regnier M, Mullier F, de Saint-Hubert M. Inappropriate low dosing of direct oral anticoagulants in older patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: impact on plasma drug levels. Thromb Res. 2021;201:139–42.
Gendron N, Chocron R, Billoir P, Brunier J, Camoin-Jau L, Tuffigo M, et al. Dabigatran level before reversal can predict hemostatic effectiveness of idarucizumab in a real-world setting. Front Med. 2020;2020:7.
Gommans E, Grouls RJE, Kerkhof D, Houterman S, Simmers T, Van Der Linden C. Dabigatran trough concentrations in very elderly patients. Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2021;28(4):231–3.
Gulilat M, Keller D, Linton B, Pananos AD, Lizotte D, Dresser GK, et al. Drug interactions and pharmacogenetic factors contribute to variation in apixaban concentration in atrial fibrillation patients in routine care. J Thromb Thrombol. 2020;49(2):294–303.
Ikeda K, Tachibana H. Clinical implication of monitoring rivaroxaban and apixaban by using anti-factor Xa assay in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. J Arrhythm. 2016;32(1):42–50.
Kampouraki E, Avery P, Biss T, Wynne H, Kamali F. Assessment of exposure to direct oral anticoagulants in elderly hospitalised patients. Br J Haematol. 2021;195(5):790–801.
Kryukov AV, Sychev DA, Andreev DA, Ryzhikova KA, Grishina EA, Ryabova AV, et al. Influence of ABCB1 and CYP3A5 gene polymorphisms on pharmacokinetics of apixaban in patients with atrial fibrillation and acute stroke. Pharmacogenom Personal Med. 2018;11:43–9.
Lin SY, Kuo CH, Huang TM, Peng YF, Huang CF, Tang SC, et al. Impact of different renal function equations on direct oral anticoagulant concentrations. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):23833.
Lin SY, Kuo CH, Yeh SJ, Tsai LK, Liu YB, Huang CF, et al. Real-world rivaroxaban and apixaban levels in asian patients with atrial fibrillation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020;107(1):278–86.
Mavri A, Vene N, Božič-Mijovski M, Miklič M, Söderblom L, Pohanka A, et al. Apixaban concentration variability and relation to clinical outcomes in real-life patients with atrial fibrillation. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13908.
Nissan R, Spectre G, Hershkovitz A, Green H, Shimony S, Cooper L, et al. Apixaban levels in octogenarian patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Drugs Aging. 2019;36(2):165–77.
Okata T, Toyoda K, Okamoto A, Miyata T, Nagatsuka K, Minematsu K. Anticoagulation intensity of rivaroxaban for stroke patients at a special low dosage in Japan. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:11.
Osanai H, Ajioka M, Masutomi T, Kuwayama T, Ishihama S, Sakamato Y, et al. Measurement of anti-factor xa activity in patients on apixaban for non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Circ J. 2015;79(12):2584–90.
Perlman A, Goldstein R, Choshen Cohen L, Hirsh-Raccah B, Hakimian D, Matok I, et al. Effect of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications on the risk of sub-therapeutic concentrations of direct oral anticoagulants: a retrospective cohort study. CNS Drugs. 2021;35(3):305–16.
Rizos T, Meid AD, Huppertz A, Dumschat C, Purrucker J, Foerster KI, et al. Low exposure to direct oral anticoagulants is associated with ischemic stroke and its severity. J Stroke. 2022;24(1):88–97.
Sacco M, Lancellotti S, Berruti F, Arcovito A, Bellelli A, Ricciardelli T, et al. Apixaban interacts with haemoglobin: effects on its plasma levels. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118(10):1701–12.
Siedler G, Macha K, Stoll S, Plechschmidt J, Wang R, Gerner ST, et al. Monitoring of direct oral anticoagulants plasma levels for secondary stroke prevention. J Thromb Haemost. 2022;20:1138–45.
Skripka A, Sychev D, Bochkov P, Shevchenko R, Krupenin P, Kogay V, et al. Factors affecting trough plasma dabigatran concentrations in patients with atrial fibrillation and chronic kidney disease. High Blood Pressure Cardiovasc Prevent. 2020;27(2):151–6.
Suwa M, Morii I, Kino M. Rivaroxaban or apixaban for non-valvular atrial fibrillation—efficacy and safety of off-label under-dosing according to plasma concentration. Circ J. 2019;83(5):991–9.
Suzuki S, Yamashita T, Akao M, Okumura K. Clinical implications of assessment of apixaban levels in elderly atrial fibrillation patients: J-ELD AF registry sub-cohort analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;76(8):1111–24.
Suzuki S, Yamashita T, Akao M, Okumura K. Predictors for a high apixaban level in elderly patients with atrial fibrillation prescribed reduced dose of apixaban. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;77(11):1757–8.
Testa S, Tripodi A, Legnani C, Pengo V, Abbate R, Dellanoce C, et al. Plasma levels of direct oral anticoagulants in real life patients with atrial fibrillation: results observed in four anticoagulation clinics. Thromb Res. 2016;137:178–83.
Testa S, Dellanoce C, Paoletti O, Cancellieri E, Morandini R, Tala M, et al. Edoxaban plasma levels in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: inter and intra-individual variability, correlation with coagulation screening test and renal function. Thromb Res. 2019;175:61–7.
Volbers B, Köhrmann M, Kallmünzer B, Kurka N, Breuer L, Ringwald J, et al. Dabigatran plasma levels in acute cerebrovascular events. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;25(4):877–82.
Cirincione B, Kowalski K, Nielsen J, Roy A, Thanneer N, Byon W, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of apixaban in subjects with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. CPT Pharmacometr Syst Pharmacol. 2018;7(11):728–38.
Dansirikul C, Lehr T, Liesenfeld KH, Haertter S, Staab A. A combined pharmacometric analysis of dabigatran etexilate in healthy volunteers and patients with atrial fibrillation or undergoing orthopaedic surgery. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(4):775–85.
Girgis IG, Patel MR, Peters GR, Moore KT, Mahaffey KW, Nessel CC, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: results from ROCKET AF. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;54(8):917–27.
Kaneko M, Tanigawa T, Hashizume K, Kajikawa M, Tajiri M, Mueck W. Confirmation of model-based dose selection for a Japanese phase III study of rivaroxaban in non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013;28(4):321–31.
Krekels EH, Niebecker R, Karlsson MO, Miller R, Shimizu T, Karlsson KE, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of edoxaban in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation in the ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 Study, a phase III clinical trial. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(9):1079–90.
Liesenfeld KH, Lehr T, Dansirikul C, Reilly PA, Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of the oral thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation from the RE-LY trial. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9(11):2168–75.
Liu XQ, Zhang YF, Ding HY, Yan MM, Jiao Z, Zhong MK, et al. Population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of rivaroxaban in Chinese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43:2726–34.
Salazar DE, Mendell J, Kastrissios H, Green M, Carrothers TJ, Song S, et al. Modeling and simulation of edoxaban exposure and response relationships in patients with atrial fibrillation. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(5):925–34.
Song S, Kang D, Halim AB, Miller R. Population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling analysis of intrinsic FXa and bleeding from edoxaban treatment. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;54(8):910–6.
Speed V, Green B, Roberts LN, Woolcombe S, Bartoli-Abdou J, Barsam S, et al. Fixed dose rivaroxaban can be used in extremes of bodyweight: a population pharmacokinetic analysis. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(9):2296–307.
Tanigawa T, Kaneko M, Hashizume K, Kajikawa M, Ueda H, Tajiri M, et al. Model-based dose selection for phase III rivaroxaban study in Japanese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013;28(1):59–70.
Ueshima S, Hira D, Kimura Y, Fujii R, Tomitsuka C, Yamane T, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenomics of apixaban in Japanese adult patients with atrial fibrillation. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;84(6):1301–12.
Willmann S, Zhang L, Frede M, Kubitza D, Mueck W, Schmidt S, et al. Integrated population pharmacokinetic analysis of rivaroxaban across multiple patient populations. CPT Pharmacometr Syst Pharmacol. 2018;7(5):309–20.
Yin OQ, Tetsuya K, Miller R. Edoxaban population pharmacokinetics and exposure-response analysis in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;70(11):1339–51.
Zhang F, Chen X, Wu T, Huang N, Li L, Yuan D, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban in chinese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a prospective multicenter study. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022;61:881–93.
Ueshima S, Hira D, Tomitsuka C, Nomura M, Kimura Y, Yamane T, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of apixaban linking its plasma concentration to intrinsic activated coagulation factor X activity in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation. AAPS J. 2019;21:5.
Ogata K, Mendell-Harary J, Tachibana M, Masumoto H, Oguma T, Kojima M, et al. Clinical safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the novel factor Xa inhibitor edoxaban in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;50(7):743–53.
Kreutz R, Persson PB, Kubitza D, Thelen K, Heitmeier S, Schwers S, et al. Dissociation between the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of once-daily rivaroxaban and twice-daily apixaban: a randomized crossover study. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(10):2017–28.
Stangier J, Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Ahnfelt L, Nehmiz G, Stähle H, et al. Pharmacokinetic profile of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate in healthy volunteers and patients undergoing total hip replacement. J Clin Pharmacol. 2005;45(5):555–63.
Frost C, Nepal S, Wang J, Schuster A, Byon W, Boyd RA, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of multiple oral doses of apixaban, a factor Xa inhibitor, in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;76(5):776–86.
Summary of Product Characteristics: Eliquis 2.5 mg film-coated tablets. 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/eliquis-epar-product-information_en.pdf.
Shimizu T, Tachibana M, Kimura T, Kumakura T, Yoshihara K. Population pharmacokinetics of edoxaban in japanese atrial fibrillation patients with severe renal impairment. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2017;6(5):484–91.
Mendell J, Shi M. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) profiles of edoxaban in healthy post-menopausal or surgically sterile females, and healthy elderly males. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:461.
Frost CE, Song Y, Shenker A, Wang J, Barrett YC, Schuster A, et al. Effects of age and sex on the single-dose pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of apixaban. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015;54(6):651–62.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Roth A, Mueck W. The influence of age and gender on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban-an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53(3):249–55.
Stangier J. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oral direct thrombin?? Inhibitor dabigatran etexilate. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47(5):285–95.
Okada M, Inoue K, Tanaka N, Sakata Y, Akao M, Yamashita T, et al. Clinical outcomes of very elderly patients with atrial fibrillation receiving on-label doses of apixaban: J-ELD AF registry subanalysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10:15.
Van Der Linden L, Decoutere L, Walgraeve K, Milisen K, Flamaing J, Spriet I, et al. Combined use of the rationalization of home medication by an adjusted STOPP in older patients (RASP) list and a pharmacist-led medication review in very old inpatients: impact on quality of prescribing and clinical outcome. Drugs Aging. 2017;34(2):123–33.
de Groot CP, Perdigao AL, Deurenberg P. Longitudinal changes in anthropometric characteristics of elderly Europeans. SENECA investigators. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1996;50(Suppl 2):S9-15.
Newman AB, Yanez D, Harris T, Duxbury A, Enright PL, Fried LP, et al. Weight change in old age and its association with mortality. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001;49(10):1309–18.
Candeloro M, Di Nisio M, Potere N, Di Pizio L, Secinaro E, De Flaviis C, et al. Frailty phenotype as a predictor of bleeding and mortality in ambulatory patients receiving direct oral anticoagulants. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2022;70(12):3503–12.
Yamamoto T, Yamashita K, Miyamae K, Koyama Y, Izumimoto M, Kamimura Y, et al. The influence of frailty under direct oral anticoagulant use in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Asia. 2019;11(2): e011212.
De Simone V, Mugnolo A, Zanotto G, Morando G. Direct oral anticoagulants for patients aged over 80 years in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: the impact of frailty. J Cardiovasc Med. 2020;21(8):562–9.
Hilmer SN, Kirkpatrick CMJ. New Horizons in the impact of frailty on pharmacokinetics: latest developments. Age Ageing. 2021;50(4):1054–63.
Verrest L, Wilthagen EA, Beijnen JH, Huitema ADR, Dorlo TPC. Influence of malnutrition on the pharmacokinetics of drugs used in the treatment of poverty-related diseases: a systematic review. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021;60(9):1149–69.
Reilly PA, Lehr T, Haertter S, Connolly SJ, Yusuf S, Eikelboom JW, et al. The effect of dabigatran plasma concentrations and patient characteristics on the frequency of ischemic stroke and major bleeding in atrial fibrillation patients: the RE-LY trial (Randomized Evaluation of Long-Term Anticoagulation Therapy). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(4):321–8.
Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, Morrow DA, Murphy SA, Kuder JF, et al. Association between edoxaban dose, concentration, anti-Factor Xa activity, and outcomes: an analysis of data from the randomised, double-blind ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 trial. Lancet. 2015;385(9984):2288–95.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Wensing G, Voith B, Zuehlsdorf M. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of BAY 59–7939—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—after multiple dosing in healthy male subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2005;61(12):873–80.
Sturkenboom MGG, Märtson A-G, Svensson EM, Sloan DJ, Dooley KE, Van Den Elsen SHJ, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and bayesian dose adjustment to advance TDM of anti-TB drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021;60(6):685–710.
Brooks E, Tett SE, Isbel NM, Staatz CE. Population pharmacokinetic modelling and bayesian estimation of tacrolimus exposure: is this clinically useful for dosage prediction yet? Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(11):1295–335.
Chan N, Sager PT, Lawrence J, Ortel T, Reilly P, Berkowitz S, et al. Is there a role for pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic-guided dosing for novel oral anticoagulants? Am Heart J. 2018;199:59–67.
Stocker SL, Carland JE, Reuter SE, Stacy AE, Schaffer AL, Stefani M, et al. Evaluation of a pilot vancomycin precision dosing advisory service on target exposure attainment using an interrupted time series analysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2021;109(1):212–21.
Eikelboom JW, Quinlan DJ, Hirsh J, Connolly SJ, Weitz JI. Laboratory monitoring of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant use in patients with atrial fibrillation. JAMA Cardiol. 2017;2(5):566.
Gosselin R, Adcock D, Bates S, Douxfils J, Favaloro E, Gouin-Thibault I, et al. International council for standardization in haematology (ICSH) recommendations for laboratory measurement of direct oral anticoagulants. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118(03):437–50.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Chayenne Van Meel and Eline Vancoppenolle, the biomedical reference librarians of the KU Leuven Libraries—2Bergen—learning Centre Désiré Collen (Leuven, Belgium), for their help in providing the assistance with the search strategy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This review article receives no specific funding. AEE is supported by AGePOP, a Horizon 2020 research and innovation program; Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant (No. 956146). TV is supported by a research Grant from FWO No. 1843423N
Conflict of Interest
Angela Elma Edwina, Nada Dia, Erwin Dreesen, Thomas Vanassche, Peter Verhamme, Isabel Spriet, Lorenz Van der Linden, Jos Tournoy declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
AEE, JT, LVdL provided the concept for this review. AEE and ND performed the literature search and data analysis. AEE drafted the original manuscript. ND, ED, TV, PV, IS, LVdL, JT critically reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Edwina, A.E., Dia, N., Dreesen, E. et al. Insights into the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Older Adults with Atrial Fibrillation: A Structured Narrative Review. Clin Pharmacokinet 62, 351–373 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-023-01222-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-023-01222-w