Abstract
Purpose
Previous functional neuroimaging studies showed that the brainstem may have an important role in migraine and recently, DTI studies demonstrated that structural alterations in migraineurs may extend beyond the normal appearing brain tissue. The aim of our study was to find out if DTI may detect any abnormality during the spontaneous migraine attacks.
Methods
The DTI images obtained in a 3T system during spontaneous migraine episodes. Patients with any systemic or metabolic disorder and abnormal signal intensity in conventional sequences were excluded. We measured the FA and ADC values of red nuclei, periaquaductal gray matter, thalami, posterior limbs of internal capsules and subcortical white matter. Fifteen healthy volunteers served as control group.
Results
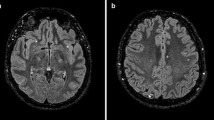
Fourteen patients enrolled in the study. The only site where we found an abnormality was the red nuclei, where the ADC values in migraineurs were statistically higher than in healthy volunteers. There was no statistical correlation between the DTI measurements and patients’ ages, duration of disease, frequency of attacks and localization of pain.
Conclusion
Our findings supported the findings of previous functional neuroimaging studies, which concluded that the brainstem might have a role in the pathogenesis of a migraine episode. We think that the increase of ADC values in red nuclei may reflect vasogenic edema, which cannot be detected in conventional sequences. However, the exact underlying mechanism for this observation is unclear and we do not know whether these changes are responsible for triggering an attack or if they are the consequents of the attack itself.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cutrer FM. Pathophysiology of migraine. Semin Neurol. 2010;30:120–30.
Lipton RB, Bigal ME. Migraine: epidemiology, impact, and risk factors for progression. Headache. 2005;45 Suppl 1:S3–13.
Woods RP, Iacoboni M, Mazziotta JC. Brief report: bilateral spreading cerebral hypoperfusion during spontaneous migraine headache. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:1689–92.
Bednarczyk EM, Remler B, Weikart C, Nelson AD, Reed RC. Global cerebral blood flow, blood volume, and oxygen metabolism in patients with migraine headache. Neurology. 1998;50:1736–40.
Cutrer FM, Sorensen AG, Weisskoff RM, Ostergaard L, Sanchez del Rio M, Lee EJ, et al. Perfusion-weighted imaging defects during spontaneous migrainous aura. Ann Neurol. 1998;43:25–31.
Sanchez del Rio M, Bakker D, Wu O, Agosti R, Mitsikostas DD, Ostergaard L, et al. Perfusion weighted imaging during migraine: spontaneous visual aura and headache. Cephalalgia. 1999;19:701–7.
Hadjikhani N, Sanchez del Rio M, Wu O, Schwartz D, Bakker D, Fischl B, et al. Mechanisms of migraine aura revealed by functional MRI in human visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:4687–92.
Welch KM, Nagesh V, Aurora SK, Gelman N. Periaqueductal gray matter dysfunction in migraine: cause or the burden of illness? Headache. 2001;41:629–37.
Weiller C, May A, Limmroth V, Jüptner M, Kaube H, Schayck RV, et al. Brain stem activation in spontaneous human migraine attacks. Nat Med. 1995;1:658–60.
Bahra A, Matharu MS, Buchel C, Frackowiak RS, Goadsby PJ. Brainstem activation specific to migraine headache. Lancet. 2001;357:1016–7.
Afridi SK, Matharu MS, Lee L, Kaube H, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS, et al. A PET study exploring the laterality of brainstem activation in migraine using glyceryl trinitrate. Brain. 2005;128:932–9.
Afridi SK, Giffin NJ, Kaube H, Friston KJ, Ward NS, Frackowiak RS, et al. A positron emission tomographic study in spontaneous migraine. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1270–5.
Denuelle M, Fabre N, Payoux P, Chollet F, Geraud G. Hypothalamic activation in spontaneous migraine attacks. Headache. 2007;47:1418–26.
Nucifora PG, Verma R, Lee SK, Melhem ER. Diffusion-tensor MR imaging and tractography: exploring brain microstructure and connectivity. Radiology. 2007;245:367–84.
Jellison BJ, Field AS, Medow J, Lazar M, Salamat MS, Alexander AL. Diffusion tensor imaging of cerebral white matter: a pictorial review of physics, fiber tract anatomy, and tumor imaging patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:356–69.
Mukherjee P, Berman JI, Chung SW, Hess CP, Henry RG. Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: theoretic underpinnings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:632–41.
Rocca MA, Colombo B, Inglese M, Codella M, Comi G, Filippi M. A diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging study of brain tissue from patients with migraine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003;74:501–3.
Rocca MA, Pagani E, Colombo B, Tortorella P, Falini A, Comi G, et al. Selective diffusion changes of the visual pathways in patients with migraine: a 3-T tractography study. Cephalalgia. 2008;28:1061–8.
Ceccarelli A, Rocca MA, Falini A, Tortorella P, Pagani E, Rodegher M, et al. Normal-appearing white and grey matter damage in MS. A volumetric and diffusion tensor MRI study at 3.0 Tesla. J Neurol. 2007;254:513–8.
Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. International classification of headache disorders. 2nd ed. Cephalalgia. 2004;24 Suppl 1:8–152.
Welch KM, Cao Y, Aurora S, Wiggins G, Vikingstad EM. MRI of the occipital cortex, red nucleus, and substantia nigra during visual aura of migraine. Neurology. 1998;51:1465–9.
Cao Y, Aurora SK, Nagesh V. Functional MRI-BOLD of brainstem structures during visually triggered migraine. Neurology. 2002;59:72–8.
de Carvalho Rangel C, Hygino Cruz LC Jr, Takayassu TC, Gasparetto EL, Domingues RC. Diffusion MR imaging in central nervous system. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2011;19:23–53.
Le Bihan D. Looking into the functional architecture of the brain with diffusion MRI. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:469–80.
Cotran RS, Kumar V, Robbins S. Robbins pathologic basis of disease. 4th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 1989.
Brubaker LM, Smith JK, Lee YZ, Lin W, Castillo M. Hemodynamic and permeability changes in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome measured by dynamic susceptibility perfusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26:825–30.
Maclullich AM, Ferguson KJ, Reid LM, Deary IJ, Starr JM, Seckl JR, et al. Higher systolic blood pressure is associated with increased water diffusivity in normal-appearing white matter. Stroke. 2009;40:3869–71.
Kruit MC, Launer LJ, Overbosch J, van Buchem MA, Ferrari MD. Iron accumulation in deep brain nuclei in migraine: a population-based magnetic resonance imaging study. Cephalalgia. 2009;29:351–9.
Haris M, Gupta RK, Husain N, Hasan KM, Husain M, Narayana PA. Measurement of DTI metrics in hemorrhagic brain lesions: possible implication in MRI interpretation. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24:1259–68.
Awasthi R, Gupta RK, Trivedi R. Diffusion tensor MR imaging in children with pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation and their siblings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:442–7.
Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Rohlfing T, Sullivan EV. Diffusion tensor imaging of deep gray matter brain structures: effects of age and iron concentration. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31:482–93.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kara, B., Kiyat Atamer, A., Onat, L. et al. DTI Findings During Spontaneous Migraine Attacks. Clin Neuroradiol 23, 31–36 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-012-0165-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-012-0165-y