Abstract
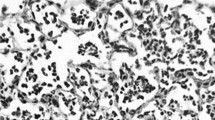
Administering recombinant interleukin-1β (IL-1β) intratracheally caused lung neutrophil accumulation and lung injury in hamsters. The percentage of leukocytes that were neutrophils increased progressively in lavages from lungs of hamsters given 25, 50, or 100 ng IL-1β intratracheally 2 h before. Lung injury, reflected by increased lung lavage protein concentrations and lung lavage hemoglobin concentrations, increased 2 h after administering 100 ng IL-1β. Lung injury, reflected by lung wet weight/body weight ratios, followed similar patterns, with significant increases occurring 2 h after insufflating 50 or 100 ng IL-1. Our results indicate that increased concentrations of IL-1β in lung airways can cause neutrophil recruitment and lung injury in hamsters. This mechanism may contribute to the development of lung neutrophil accumulation and lung injury that characterizes ARDS patients who have increased airway levels of IL-1β.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Repine, J. E. 1992. Scientific perspectives on adult respiratory distress syndrome.Lancet 339:466–469.
Dinarello, C. A., andS. M. Wolff. 1993. The role of interleukin-1 in disease.N. Engl. J. Med. 328:106–113.
Elias, J. A., B. Freundlich, J. A. Kern, andJ. Rosenbloom. 1990. Cytokine networks in the regulation of inflammation and fibrosis in the lung.Chest 97(6):1439–1445.
Jacobs, R. F., D. R. Tabor, A. W. Burks, andG. D. Campbell. 1989. Elevated interleukin-1 release by human alveolar macrophages during the adult respiratory distress syndrome.Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 140(6):1686–1692.
Siler, T. M., J. E. Swierkosz, T. M. Hyers, A. A. Fowler, andR. O. Webster. 1989. Immunoreactive interleukin-1 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in high-risk patients and patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome.Exp. Lung Res. 15(6):881–894.
Suter, P. M., S. Suter, E. Girardin, P. Roux-Lombard, G. E. Gran, andJ. Dayer. 1992. High bronchoalveolar levels of tumor necrosis factor and its inhibitors, interleukin-1, interferon and elastase, in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome after trauma, shock, or sepsis.Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 145:1016–1022.
Faccioli, L. H., G. E. Souza, F. Q. Cunha, S. Poole, andS. H. Ferreira. 1990. Recombinant interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor induce neutrophil migration in vivo by indirect mechanisms.Agents Actions 30:344–349.
Okusawa, S., J. A. Gelfand, T. Ikejima, R. J. Connolly, andC. A. Dinarello. 1988. Interleukin-1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition.J. Clin. Invest. 81(4):1162–1172.
Leff, J. A., J. W. Baer, M. E. Bodman, J. M. Kirkman, P. F. Shanley, L. M. Patton, D. M. Guidot, C. J. Beehler, J. M. McCord, andJ. E. Repine. 1994. Interleukin-1-induced lung neutrophil accumulation and oxygen metabolite mediated lung leak in rats.J. Appl. Physiol. 76:151–157.
Ulich, T. R., S. M. Yin, K. Z. Guo, J. Del Castillo, S. P. Eisenberg, andR. C. Thompson. 1991. The intratracheal instillation of cytokines. III. The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist inhibits endotoxin and IL-1-induced acute inflammation.Am. J. Pathol. 138:521–524.
Heidel, J. R., H. M. Sassenfeld, C. R. Maliszcrodki, R. M. Silflow, P. E. Baker, S. M. Taylor, andR. W. Leid. 1990. Functional studies of bovine alveolar neutrophils elicited with recombinant bovine IL-1 beta.J. Immunol. 144:1037–1041.
Furie, M. B., andD. D. McHugh. 1989. Migration of neutrophils across endothelial monolayers is stimulated by treatment of the monolayers with interleukin-1 or tumor necrosis factor-alpha.J. Immunol. 143(10):3309–3317.
Bevilacqua, M. P., J. S. Pober, M. E. Wheeler, R. S. Cotran, andM. A. Gimbrone. 1985. Interleukin-1 activation of vascular endothelium. Effects of procoagulant activity and leukocyte adhesion.Am. J. Pathol. 1212:394–403.
Kharazimi, A., H. Nielsen, andK. Bendtzen. 1988. Recombinant interleukin-1α andβ prime human monocyte superoxide production but have no effect on chemotaxis and oxidative burst response of neutrophils.Immunobiology 177:32–39.
Matsubara, T., andM. Ziff. 1986. Increased superoxide anion release from human endothelial cells in response to cytokines.J. Immunol. 137:3295–3298.
Ozaki, Y., T. Ohashi, andS. Kume. 1987. Potentiation of neutrophil function by recombinant DNA-produced interleukin-1α.J. Leukocyte Biol. 42(6):621–627.
Schroder, J. M., M. Sticherling, H. H. Henneicke, W. C. Preissner, andE. Christophers. 1990. IL-1 alpha or tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulate release of three NAP-1/IL-8-related neutrophil chemotactic proteins in human dermal fibroblasts.J. Immunol. 144(6):2223–2232.
Wankowicz, Z., P. Megyeri, andA. Issekutz. 1988. Synergy between tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 in the induction of polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration during inflammation.J. Leukocyte Biol. 43(4):349–356.
Leff, J. A., C. P. Wilke, B. M. Hybertson, P. F. Shanley, C. J. Beehler, andJ. E. Repine. 1993. Post-insult treatment with N-acetylcysteine decreases interleukin-1-induced lung neutrophil sequestration and oxidative lung leak in rats.Am. J. Physiol. 265:501–506.
Guidot, D. M., E. E. Stevens, M. J. Repine, A. E. Lucca-Broco, andJ. E. Repine. 1994. Intratracheal but not intravascular interleukin-1 causes acute edematous injury in isolated neutrophil-perfused rat lungs through an oxygen radical mediated mechanism.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 12:605–609.
Repine, M. J., D. M. Guidot, andJ. E. Repine. 1994. Neutrophil derived NADPH oxidase and lipoxygenase products mediate damage in isolated neutrophil perfused rat lungs given interleukin-8 (IL-8) intratracheally.Clin. Res. 42:5A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patton, L.M., Saggart, B.S., Ahmed, N.K. et al. Interleukin-1β-induced neutrophil recruitment and acute lung injury in hamsters. Inflammation 19, 23–29 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01534377
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01534377